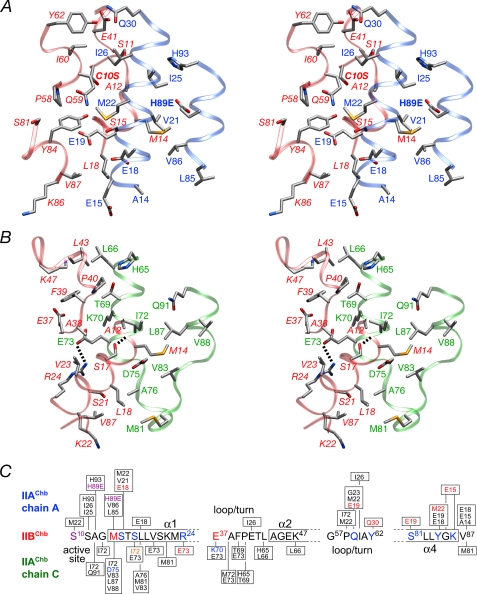
FIGURE 4.
The IIAChb*(H89E)-IIBChb(C10S) interface. A, stereoview of the interface between the A subunit of IIAChb*(H89E) and IIBChb(C10S) with the respective backbones shown as transparent blue and red ribbons, respectively. B, stereoview of the interface between the C subunit of IIAChb*(H89E) and IIBChb(C10S) with the respective backbones shown as transparent green and red ribbons, respectively. The dashed lines indicate intermolecular hydrogen bonds or salt bridges. The side chain atoms are colored according to atom type; carbon, gray; nitrogen, blue; oxygen, red. Residues of IIBChb(C10S) are labeled in italics. C, diagrammatic representation of the intermolecular contacts between the A and C subunits of IIAChb*(H89E) and IIBChb(C10S). Residues involved in side chain-side chain electrostatic interactions are colored in blue (donor) or red (acceptor). Ile-72 of the C subunit of IIAChb*(H89E) is colored in orange because its backbone carbonyl accepts a hydrogen bond from Ser-17 of IIBChb(C10S). The active site residues, H89E of IIAChb*(H89E), and C10S of IIBChb(C10S) are colored purple.