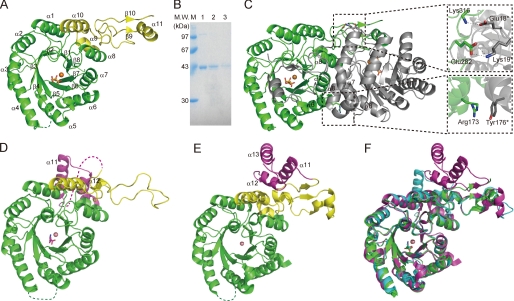
FIGURE 1.
Structures of TtHCS. A, monomer structure of the TtHCS·Cu2+·α-KG complex. The (β/α)8 TIM barrel domain and C-terminal small domain I are in green and yellow, respectively. Metal Cu2+ is shown as orange spheres and α-KG is shown as orange sticks. The disordered region (Ser-98 to His-105) is shown as a dotted line. B, SDS-PAGE of TtHCS proteins dissolved from crystals. A single crystal was dissolved in 20 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, and applied to 15% SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, freshly purified TtHCS-Chis; lane 2, TtHCS·Cu2+·α-KG dissolved from a crystal; lane 3, TtHCS·Cu2+·HC dissolved from a crystal. C, dimer structure of TtHCS·Cu2+·α-KG complex. Bound Cu2+ ion is shown as orange spheres, and α-KG is shown as sticks. One monomer is shown in green, and the adjacent subunit is shown in gray. Intersubunit hydrogen bonds are shown in enlarged insets. D, monomer structure of the TtHCS·Co2+·Lys complex. The (β/α)8 TIM barrel domain, C-terminal small domain I, and C-terminal small domain II are shown in green, yellow, and purple, respectively. Metal Co2+ is shown as pink spheres, and bound lysine is shown as magenta sticks. The disordered region (Leu-317 to Leu-336) is shown as a dotted line. E, monomer structure of the SpHCS·Zn2+complex. Domain colors are the same as in D. Metal Zn2+ is shown as pink spheres. F, superposition of the structure of the TtHCS·Cu2+·α-KG complex (green) with those of the TtHCS·Co2+·Lys complex (cyan) and the SpHCS·Zn2+ complex (magenta). α-KG and Lys are shown as green and cyan sticks, respectively.