Figure 1.
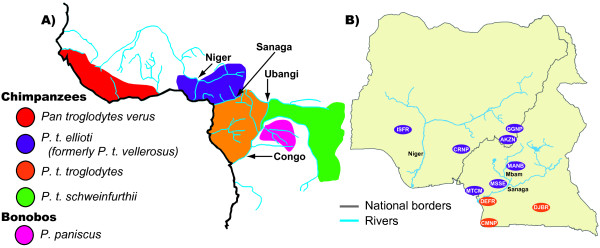
Chimpanzee subspecies and georeferenced DNA sampling distributions. A) Distribution of chimpanzee subspecies. Chimpanzees belong to a single species (Pan troglodytes) that is divided into four subspecies [1]. Phylogenetic analyses of mtDNA suggest that these subspecies are divided into two geographically and genetically defined groups that split about 0.5 mya: a western African group (P. t. verus and P. t. ellioti [22] [known until recently as P. t. vellerosus [23]) and a central/eastern African group (P. t. troglodytes and P. t. schweinfurthii) [24]. A phylogeographic break between these two groups occurs at the Sanaga River in central Cameroon, separating populations of P. t. ellioti north of the river from P. t. troglodytes south of the river. However, the Sanaga does not stop dispersal between subspecies completely because some gene flow between them occurs near the confluence of the Sanaga and its main tributary, the Mbam River [24,28]. B) Map of Cameroon and Nigeria showing collection sites of georeferenced chimpanzee DNA samples. Sampling sites shown on the map are: Ise Forest Reserve (ISFR), Cross River National Park (CRNP), Akoh Zanto (AKZN), Gashaka Gumti National Park (GGNP), Mount Cameroon (MTCM), Mosse (MSSE), Manb'ra (MANB), Douala-Edea Forest Reserve (DEFR), Campo-Ma'an National Park (CMNP) and Dja Biosphere Reserve (DJBR).
