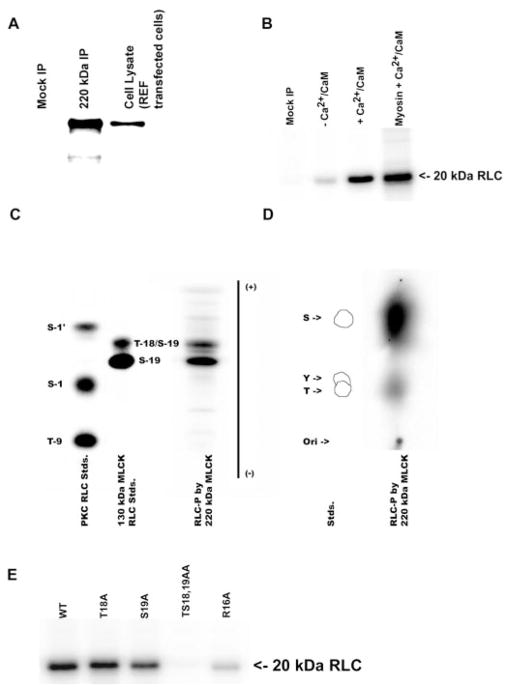
Fig. 2.
Phosphorylation of regulatory light chains (RLCs) by 220-kDa MLCK. A: immunoprecipitation and detection of the 220-kDa MLCK expressed in REF-52 cells with a plasmid encoding 220-kDa MLCK (220-kDa IP) or transfected with vector alone (Mock IP). The immunoprecipitated 220-kDa MLCK was detected by Western blotting using K36 monoclonal antibody. B: purified wild-type RLCs and platelet myosin [nonmuscle myosin heavy chain (NMHC)-IIA] were incubated with immunopurified 220-kDa MLCK in the presence (+) or absence (−) of Ca2+/calmodulin (Ca2+/CaM) for 30 min, and 32P-labeled light chains were analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. C: 1-dimensional tryptic peptide map of phosphorylation sites in RLCs after phosphorylation by immunoprecipitated 220-kDa MLCK. Control lanes are protein kinase C (PKC) phosphorylated RLC standards (Stds) and recombinant 150-kDa rabbit MLCK (MLCK) prepared as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. S-1′, S-1, and T-9 are sites phosphorylated by PKC, and S-19 and T-18 are sites phosphorylated by MLCK. Two phosphopeptides corresponding to S-19 (monophosphorylated) and S-19/T-18 (diphosphorylated) RLCs are detected in the 220-kDa MLCK lane. D: phosphoamino acid analysis of 32P incorporation into RLCs by 220-kDa MLCK. The standards are phosphoserine (S), phosphothreonine (T), and phosphotyrosine (Y). Phosphoamino acid analysis demonstrates that both S and T residues are phosphorylated by 220-kDa MLCK. E: 220-kDa MLCK-catalyzed phosphorylation of WT and mutant recombinant RLCs. The immunoprecipitated 220-kDa MLCK phosphorylates WT and T18A, S19A, and R16A mutant RLCs and does not phosphorylate the TS1819AA mutant RLC.