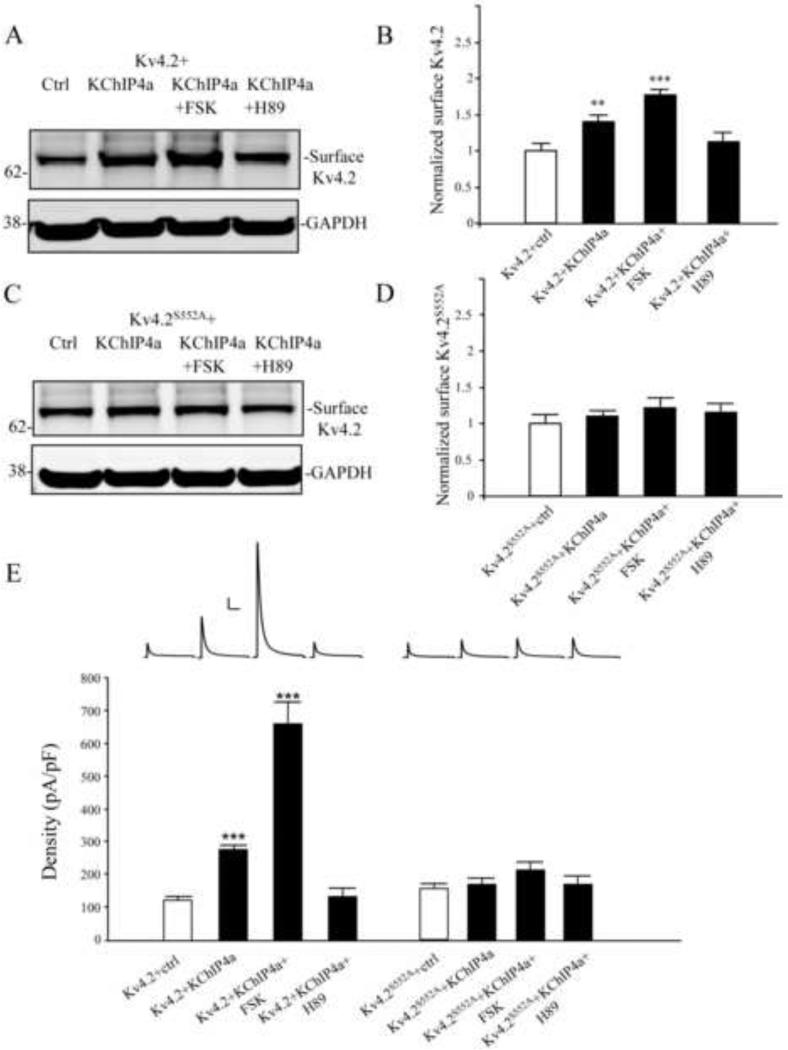
Figure 4.
PKA activation enhances the surface expression of Kv4.2 by KChIP4a (A-B) Biotinylation assay showed surface Kv4.2 were increased about 1.5 fold by co-expressed with KChIP4a in COS7 cells. Long-term treatment with forskolin (10 μM, 24 hr) greatly enhances the surface expression of Kv4.2 compared to Kv4.2 alone, but it was blocked by the PKA inhibitor H89 (10 μM for 1 hr). GAPDH served as a loading control. (C-D) Surface expression of the Kv4.2 phospho-mutant S552A (Kv4.2S552A) was not enhanced either with KChIP4a co-expression or forskolin (10 μM, 24hr). Error bars represent S.E.M. (E) In electrophysiological recording from HEK293 cells, peak current density of Kv4.2-mediated currents were increased about 2 fold by co-expression with KChIP4a (n = 15). Long-term treatment with forskolin (10 μm, 24 hr, n = 10) showed a significant increase (~5-fold) of the peak current density compared to Kv4.2 alone, but it was blocked subsequent application of the PKA inhibitor H89 (10 μm, 1hr, n = 11). Peak current density enhancement by KChIP4a was not found in HEK cells expressing the Kv4.2S552A mutant (n = 10) or forskolin (10 μM, 24hr, n = 10) and H89 (10 μM, 1hr, n = 10) treatment compared to Kv4.2S552A alone. Error bars represent S.E.M. Scale bars: 1 nA, 100 ms.