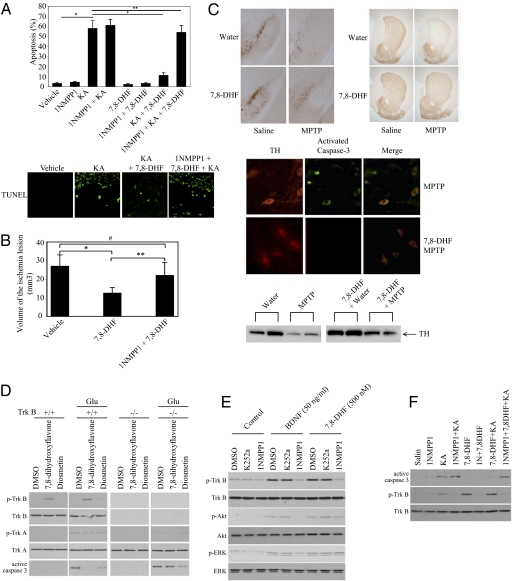
Fig. 4.
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone is neuroprotective in models of neuronal injury. (A ) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone decreases KA-induced apoptosis in mouse brain in a TrkB-dependent manner. TrkB F616A mice were injected with various indicated solutions, and the brain slides were analyzed with TUNEL assay. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (ANOVA; n = four to five mice/group; #, P < 0.005; *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.1;). (B) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone diminishes stroke damage in a TrkB-dependent manner. Infarct volumes after 24 h MCAO were substantially decreased by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Pretreatment with 1NMPP1 impaired the protective effect of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (One way ANOVA, n = 8–12 mice/group; #, not significant; *, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.02). (C) 7,8-Dihydroflavone is neuroprotective in a model of Parkinson disease. Mice were administered 7,8-dihydroxyflavone in drinking water for 14 days. On day 7, the mice were given two doses of MPTP (20 mg/kg, i.p.) 2 h apart. On day 14, mice were killed. Immunostaining (substantia nigra, striatum) (Upper panels) and immunoblotting (striatal homogenates, lanes from the same gel at the same exposure) of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) (Lower panels), and fluorescence microscopy of activated caspase-3 in TH+ nigral neurons revealed reduced toxicity in 7,8-dihydroxyflavone-treated mice (Lower panels). (D) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone prevents glutamate-triggered neuronal apoptosis in wild-type but not TrkB-null neurons. Cortical neurons were prepared from the P0 pups. The neurons were pretreated with indicated compounds, followed by glutamate (50 μM). The cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (E) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone selectively activates TrkB F616A, which can be blocked by 1NMPP1. The primary cortical cultures were pretreated for 30 min with either K252a (100 nM) or 1NMPP1 inhibitor (100 nM), followed by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Immunoblotting with cell lysates was performed. (F) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone suppresses KA-induced neuronal cell death in TrkB F616A mutant mice, which can be blocked by 1NMPP1.