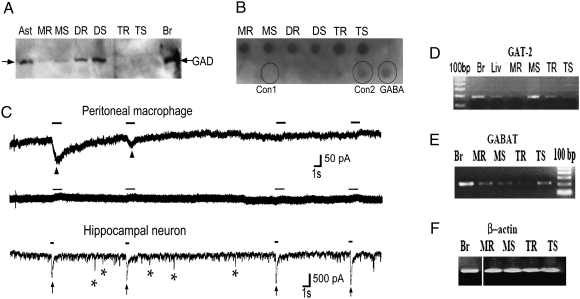
Fig. 1.
A GABAergic system is present in the immune system. (A) Macrophages and DCs were purified and stimulated with LPS, and CD4+ T cells were stimulated with α-CD3 and α-CD28 for 24–48 h. GAD enzyme was detected by immunoblotting in resting (MR or DR or TR) or stimulated (MS or DS or TS) peritoneal macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells, respectively. Astrocytes (Ast) and brain extract (Br) were used as positive controls. (B) GABA secreted into conditioned media supernatant over purified immune cells, stimulated as above, was measured by dot blot. Controls are commercial pure GABA (2 μM) and same volume growth media used without cells: serum-free RPMI used for growth of DCs and macrophages (Con1) or X-Vivo 20 used for growing T cells (Con2). (C) Representative trace of a voltage-clamp recording showing functional GABA receptors in peritoneal macrophages during the first 10 s of recording (Top) and showing lack of response to GABA application 20 min after the initial responses (Middle). Bottom: Hippocampal neurons cultured 14 days in vitro are used as control. Arrowheads point to currents induced by focal application of 100 μM GABA for 1-s duration (marked by solid bars) in peritoneal macrophages. Arrows point to GABA currents induced by focal application of 100 μM GABA for 0.5-s duration in hippocampal neurons. In addition, neurons show spontaneous IPSCs, some denoted by asterisks. N = 11, n = 7 for macrophages and N = 3, n = 3 for neurons, where N is the total number of cells and n is the number of cells showing responses to GABA application. (D–F) mRNA was measured by RT-PCR in immune cells stimulated as in A. GABAT is the enzyme that degrades GABA, and GAT-2, a GABA transporter. Brain (Br), liver (Liv), and β-actin are used as controls.