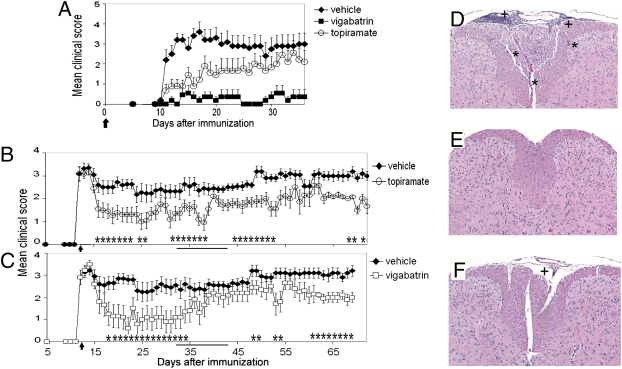
Fig. 3.
GABAergic agents ameliorate EAE. (A–C) SJL/J mice were immunized with 100 μg of PLP 139-151 in CFA. Graphs represent prevention of EAE (A) by oral treatment with topiramate (100 mg/kg per day) or vigabatrin (400 mg/kg per day) starting at the time of immunization, as indicated by the arrow; and treatment of established EAE (B and C) by oral topiramate (100 mg/kg per day) or vigabatrin (400 mg/kg per day) starting at the peak of disease, as indicated by the arrow. Data represent clinical scores, as described in Materials and Methods, mean ± SEM, representative of two independent experiments, n = 10 per group. *P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney analysis. In B and C, mice were treated daily except during days 32–42, as indicated by the solid bar, when they were treated every 3 days. (D–F) H&E-stained transverse sections of spinal cord of mice killed at the end of the experiment (day 37; A). Representative control (D), topiramate- (E), and vigabatrin-treated animals (F) are shown. *Parenchymal inflammatory foci; +meningeal inflammatory foci. 125× magnification.