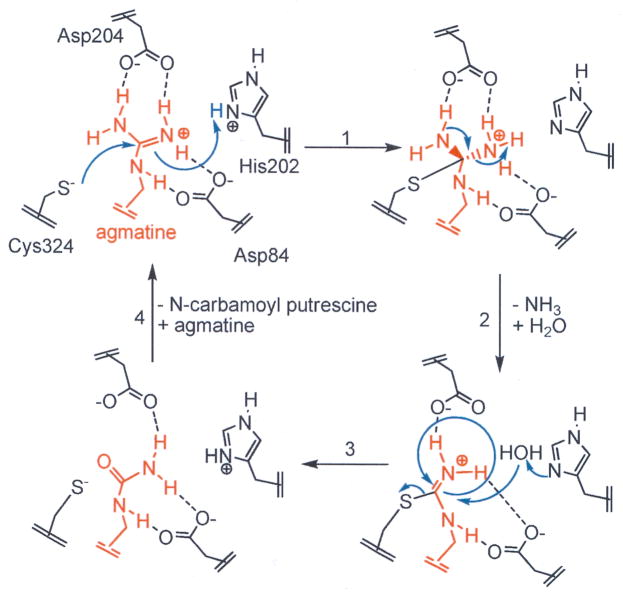
Fig. 2.
Proposed catalytic mechanism: Cys324 is the active site nucleophile and His202 acts as a general acid, donating a proton to the departing amine, leading to the formation of an S-alkyl thiouronium intermediate. His 202 activates a water molecule for nucleophilic attack on the thiouronium intermediate. This leads to the formation of a second tetrahedral intermediate that collapses to eliminate the Cys thiolate and generate NCP.