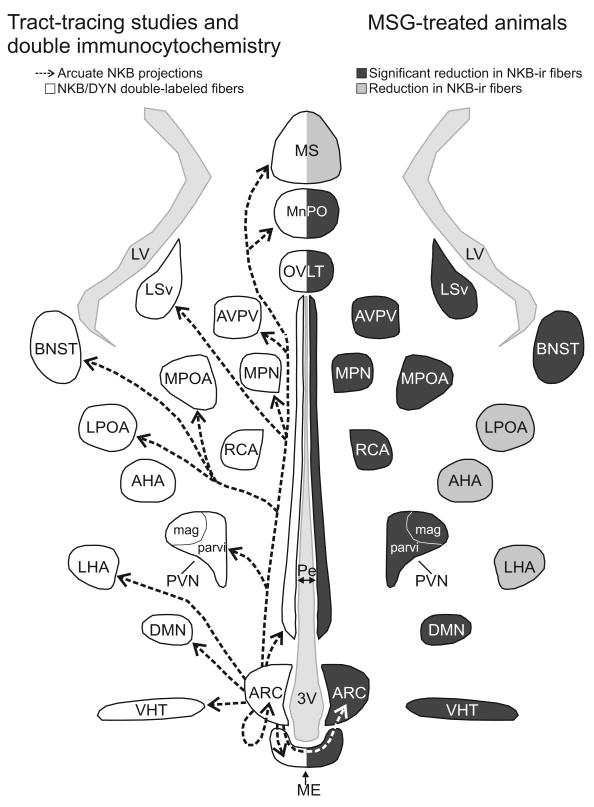
Figure 10.
Schematic diagram (horizontal plane) of arcuate NKB projections revealed by anterograde tract-tracing and NKB/dynorphin immunofluorescence (left) and MSG-ablation of arcuate NKB neurons (right). Left: The arrows indicate the location of arcuate NKB projections labeled by a BDA injection into the arcuate nucleus. The outlined areas show the where dual-labeled NKB/dynorphin-ir fibers were previously described (Burke et al., 2006). Right: The areas shaded in dark gray exhibited a significant reduction in NKB-ir fibers in MSG-treated animals. The areas shaded light gray exhibited a reduction of NKB-ir in MSG-treated animals that was not significantly different. The diverse projections of arcuate NKB neurons provide a mechanism to integrate the reproductive axis with multiple homeostatic and neuroendocrine circuits.