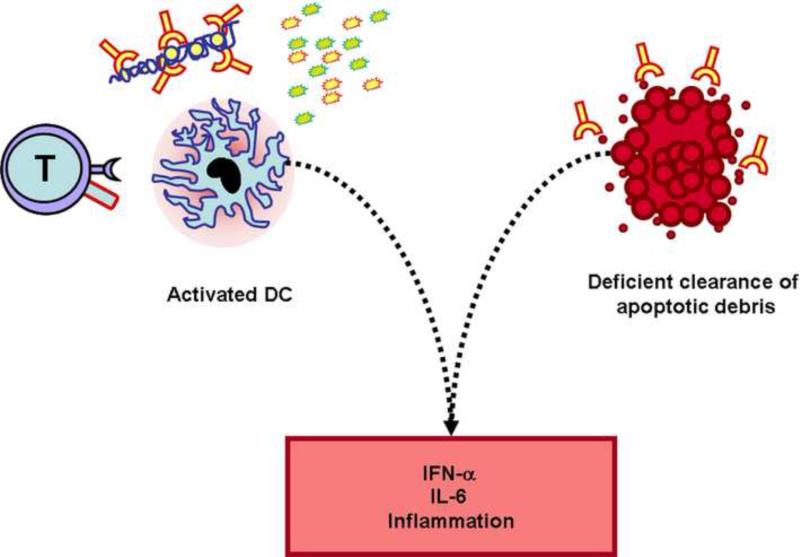
Figure 3. Activated dendritic cells induce inflammation upon exposure to apoptotic and necrotic debris.
Dendritic cells from patients with SLE are activated by T cell co-stimulatory molecules (i.e. CD40L), inflammatory cytokines, and nucleic acid-containing immune complexes. Activated DCs produce increased amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-6, IFN-α) that amplify the immune response. Apoptotic material is not recognized as anti-inflammatory and contributes to DC activation.