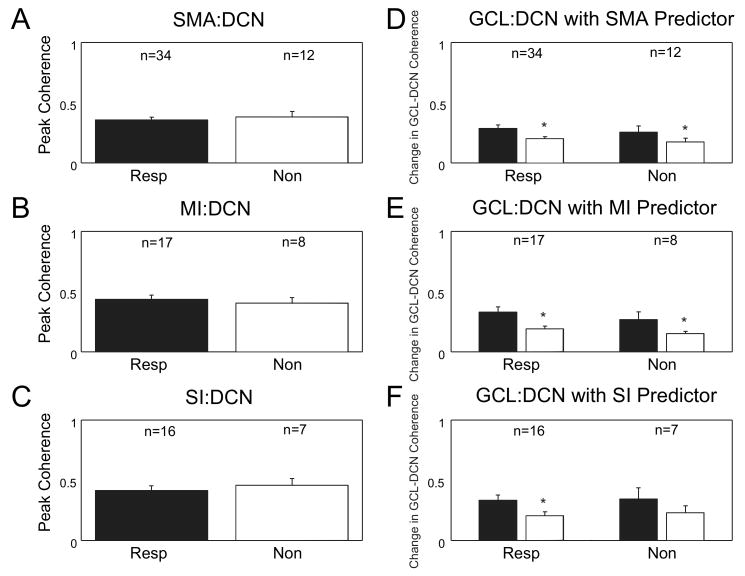
Figure 7. Cortex significantly influences coherence between the GCL and both responsive and nonresponsive DCN neurons.
A-C: The peak coherence of the different cortical areas with both responsive and nonresponsive neurons was compared. The bar graphs show no difference in the peak coherence between SMA (p = 0.62, t-test), MI (p = 0.63, t-test) or SI (p = 0.60, t-test) and responsive or nonresponsive DCN neurons to air puff stimuli to the face. D-F: A comparison of the change in coherence when the cortical signal is removed from GCL:DCN coherence shows a significant difference in the SMA (resp: p < 0.001, Wilcoxon signed rank test, nonresp: p = 0.001, Wilcoxon signed rank test), MI (resp: p < 0.001, paired t-test, nonresp: p = 0.72, paired t-test), and SI (resp: p = 0.002, paired t-test) cortical areas. Only the SI cortical signal did not significantly influence GCL:DCN coherence with nonresponsive neurons (p = 0.133, paired t-test). Standard error bars plotted in all graphs.