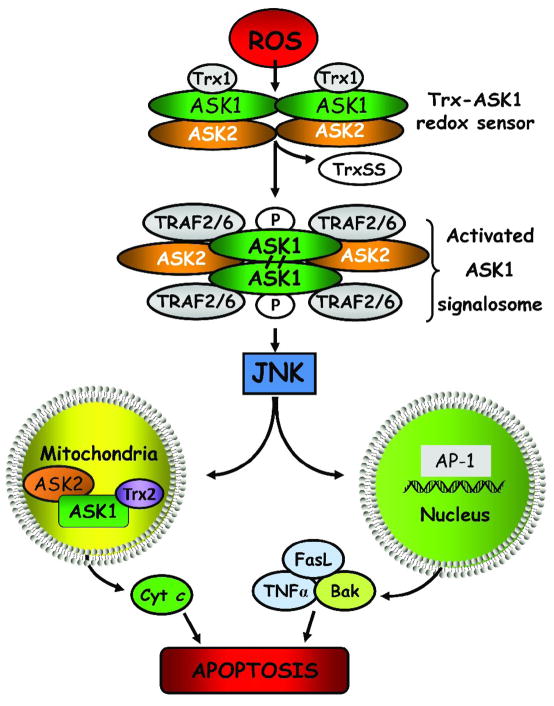
Figure 2. ROS-induced ASK1/JNK signaling and apoptosis.
Reactive oxygen species initiate Trx dissociation from the ASK1-Trx complex, the ASK1 signalosome, through oxidation of Trx redox active site. ASK1 undergoes auto-phosphorylation and covalent binding between its subunits, leading to the formation of “activated signalosome”, and recruitment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 and 6 to the complex. Activated ASK1 signals downstream JNK activation and induce apoptosis either via mitochondrial signaling or via transcription of AP-1-dependent pro-apoptotic genes. Additionally, ROS-mediated disruption of mitochondrial ASK1/ASK2/Trx2 complex induces cytochrome c release. ROS: reactive oxygen species; TRAF2/6: TNFα receptor-associated factor 2, 6; ASK1, -2: apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and 2; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase, Trx1: thioredoxin 1, reduced form; TrxSS: thioredoxin, oxidized form; Trx2: thioredoxin 2, mitochondrial enzyme; Bak: pro-apoptotic protein; cyt c, cytochrome c; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor alpha; FasL: Fas ligand.