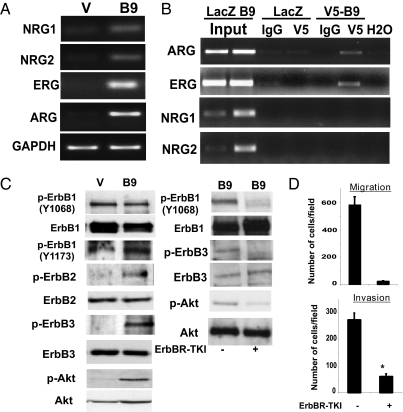
Fig. 3.
Suppression of ErbB and Akt activation inhibits HOXB9 enhanced cell motility. (A) Expression of NRGs, ERG, and ARG is increased in HOXB9-MCF10A cells. GAPDH is shown to control for equal loading. (B) ErbB ligands are transcriptional targets of HOXB9. MCF10A cells infected with LacZ and V5-tagged HOXB9 lentiviruses were analyzed by ChIP with anti-V5 and control IgG antibodies. Total lysates were used as controls for input. Precipitated DNA was subjected to PCR using primers spanning the promoter region containing the putative HOX-binding sites. (C) (Left) HOXB9 expression is associated with increased ErbB receptor phosphorylation. Proteins from vector and HOXB9-expressing cells were analyzed for activation of ErbB1, ErbB2, and ErB3, and Akt by Western blot. The lysates were also probed for total protein. (Right) Inhibition of ErbB receptor phosphorylation abolishes Akt phosphorylation. HOXB9-MCF10A cells were treated with 10 μM ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (ErbBR-TKI) for 2 h, and proteins were analyzed by Western blot to monitor ErbB receptor and Akt phosphorylation and total ErbB receptor and Akt levels. (D) Suppression of ErbB receptor and Akt phosphorylation is associated with abrogation of cell migration. Migration of ErbBR-TKI–treated HOXB9-expressing MCF10A cells was assayed. The mean was derived from cell counts of nine fields.