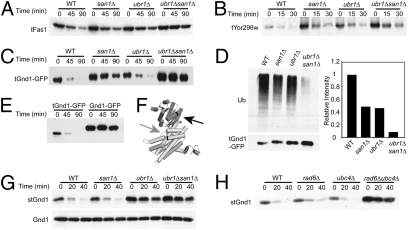
Fig. 2.
Ubr1 and San1 mediate the degradation of multiple cytoplasmic QC substrates. Cycloheximide chase and immunoblot of HA-tagged truncated Fas1 (48% total, tFas1) (A), Yor296w (39% total, tYor296w) (B), and Gnd1 (75% total, tGnd1-GFP) (C) in the indicated strains. (D) San1 and Ubr1 dependence of tGnd1-GFP ubiquitination measured by anti-GFP IP, followed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP or anti-ubiquitin (Ub) as indicated (Left). (Right) Ubiquitination immunoblotting intensities were normalized to the total precipitated tGnd1-GFP for each strain, as determined using ImageQuant TL. Results are graphed as a fraction of WT, which was set to 1.0. (E) Cycloheximide chase and anti-HA immunoblotting of 3HA-tGnd1-GFP or full-length Gnd1 fused to GFP, 3HA-Gnd1-GFP. (F) Crystal structure of full-length yeast Gnd1 created using PyMOL (19). The black arrow indicates the stGnd1 truncation point. The gray arrow indicates the tGnd1 truncation point. (G) Cycloheximide chase of 3HA-stGnd1 (Upper) or 3HA-full-length Gnd1 (Lower) in the indicated strains. Detection was with anti-HA antibodies. (H) Cycloheximide chase of stGnd1 in E2 UBC strains rad6Δ and ubc4Δ as indicated.