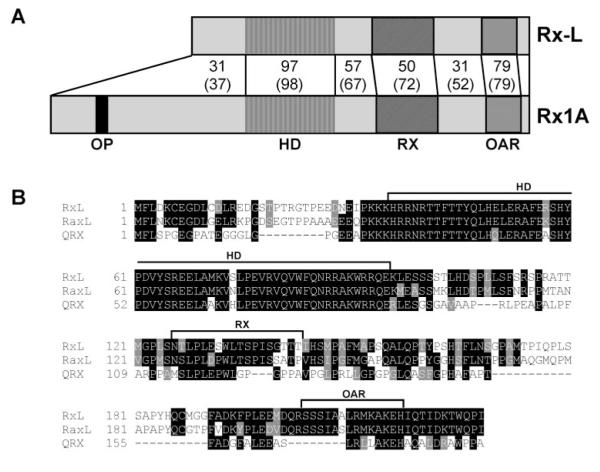
Figure 1.
Rx-L is related to Rx and similar to other Rx-like proteins. (A) Comparison of the predicted protein sequence of Xenopus laevis Rx-L and Rx1A. Rx1A and Rx-L sequences were aligned by using ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw; European Bioinformatics Institute, European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heidelberg, Germany). The percentage of amino acid identity and similarity (with respect to Rx-L) are summarized in the figure. Canonical domains are indicated. (B) Alignment of Xenopus laevis (Rx-L), chicken (RaxL), and human (QRX) Rx-like gene product sequences by ClustalW. Canonical domains are denoted with brackets above the alignment. OP, octapeptide; HD, homeodomain; RX, Rx domain; OAR, orthopedia-aristaless-Rx domain.