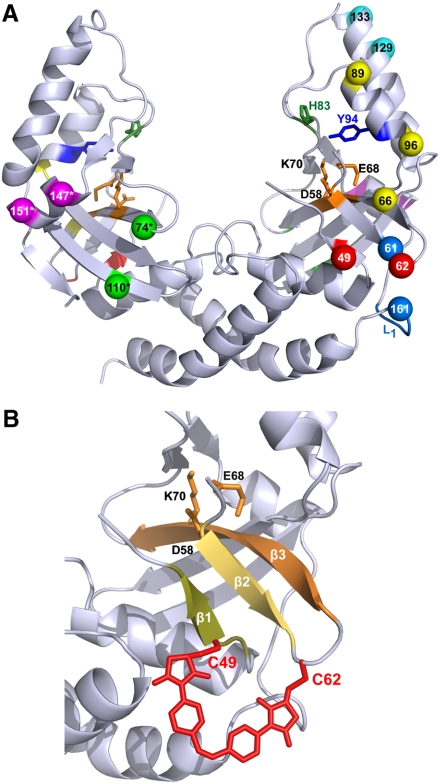
Fig. 2.
(A) The crystal structure of scPvuII (40) with the residue pairs chosen for cross-linking with azomal: (C49 C62), (C61 L1[-GSG C161-]), (C66 C96), (C74* C110*), (C89 C96), (C129 C133), and (C147* C151*). Amino acid residues of these residue pairs are depicted in identical colors. For clarity, residue pairs are shown mostly on the N-terminal half (Right), only those that are on the “backside” are shown in the C-terminal half (Left), denoted with an asterisk (*). Note that amino acid pairs were cross-linked in the N-terminal half, when only one cross-link was introduced into scPvuII, or in equivalent positions of the N- and C-terminal halves, when two cross-links were introduced (Table 1). Amino acids of residue pairs chosen for cross-linking were substituted by cysteines via site-specific mutagenesis. The amino acid residues of the active site (D58, E68, and K70) are indicated in orange. H83 (green) and Y94 (blue), which in some variants were substituted by alanine and phenylalanine, respectively, are also indicated. (B) A blow up of the region comprising β-strands β1, β2, and β3 and the catalytic center is shown, together with a model of azomal cross-linking C49 and C62.