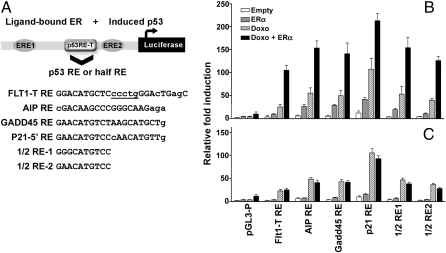
Fig. 2.
The p53 RE sequence determines the level of synergy between p53 and ERα in the FLT1 promoter motif. (A) A schematic description of the FLT1-T promoter showing the relative position of the Flt1-T RE flanked by the two identified EREs. The original 1/2 site Flt1-T RE was replaced by other 1/2 sites (previously tested in Fig. 1B) or by well-established canonical p53 REs as indicated in A. Small letters denote deviations from the consensus, although the underlined letter refers to the spacer between p53 1/2 sites. (B) The ability of these constructs to support p53 transactivation was examined using a luciferase reporter assay in U2OS cells following p53 activation by doxorubicin in the presence or absence of transfected ERα. When indicated, cells were treated with doxorubicin (0.3μg/mL) for 16 h before cell lysis. Luciferase activity was measured 48 h posttransfection and normalized for transfection efficiency. (C) Site-directed mutagenesis of the EREs in the FLT1 promoter constructs abolished the synergistic transactivation between p53 and ERα. Presented are the average-fold luciferase induction relative to the empty pGL4.26 vector ± SD (n = 3).