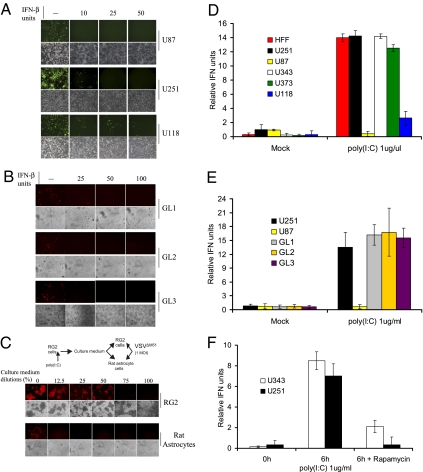
Fig. 1.
Glioma cell lines are responsive to and produce type I IFN. (A) Addition of IFN-β protects glioma cells against VSV infection. The human glioma cell lines U87, U251, and U118 were pretreated with increasing amounts of human IFN-β for 6 h before infection with VSVΔM51-GFP (MOI of 1). At 24 h after infection, GFP fluorescence and CPE were analyzed by phase-contrast and fluorescent microscopy. (B) Freshly excised glioma cells were treated as described and infected with VSVΔM51-RFP (MOI of 10). (C) Poly(I:C) stimulates type I IFN in RG2 cells and conditioned media protect cells against VSV infection. Scheme of the assay: RG2 cells were transfected with poly(I:C) dsRNA (1 μg/mL) for 6 h. Cultured medium was used to treat either RG2 or Rat astrocytes for 12 h before infection with VSVΔM51-RFP (MOI of 1). RFP fluorescence and CPE were analyzed as described. (D) Detection of type I IFN production. Human foreskin fibroblast and the indicated human glioma cell lines were treated with poly(I:C) (1 μg/mL) for 24 h. Supernatant was collected and 30 μL was used to condition HEK-Blue type I IFN cells (InvivoGen). OD was measured by colorimetric assay at 650 nm using the Quanti-Blue reagent (InvivoGen). IFN production was plotted as relative IFN units. (E) Freshly excised glioma cells were treated with poly(I:C) (1 μg/mL) for 24 h and type I IFN production was assessed as in D. (F) Rapamycin reduces the type I IFN response in glioma cells. Human glioma cell lines U251 and U343 were pretreated with DMSO or rapamycin (20 nM) for 1 h before poly(I:C) stimulation at 1 μg/mL, and HEK-Blue type I IFN colorimetric assay was performed 6 h after poly(I:C) stimulation.