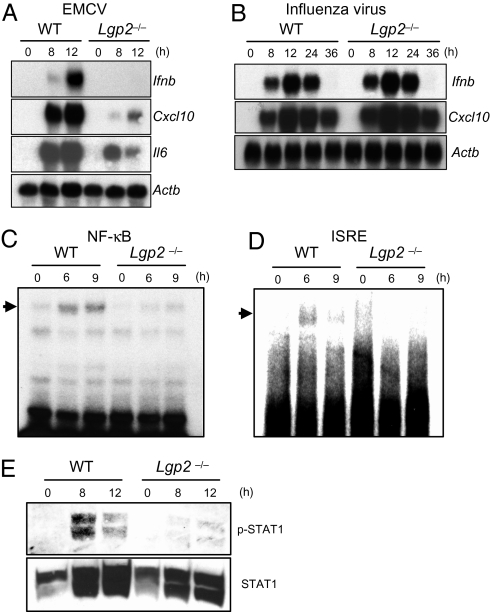
Fig. 2.
Role of LGP2 in the activation of signaling pathways leading to IFN-inducible gene expression. (A) Total RNAs extracted from WT and Lgp2 −/− macrophages infected with EMCV were subjected to Northern blot analyses for the expressions of Ifnb, Cxcl10, Il6, and Actb mRNAs. (B) WT and Lgp2 −/− MEFs were infected with influenza virus followed by isolation of the total RNA. The expressions of Ifnb, Cxcl10, and Actb mRNAs were determined by Northern blot analyses. (C and D) Nuclear extracts were prepared from WT and Lgp2 −/− macrophages infected with EMCV for the indicated periods. The binding activities of DNA to NF-κB (C) and ISREs (D) were determined by EMSAs. (E) Cell lysates were prepared from WT and Lgp2 −/− macrophages infected with EMCV and probed with anti–phospho-STAT-1 and anti-STAT1 antibodies. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments.