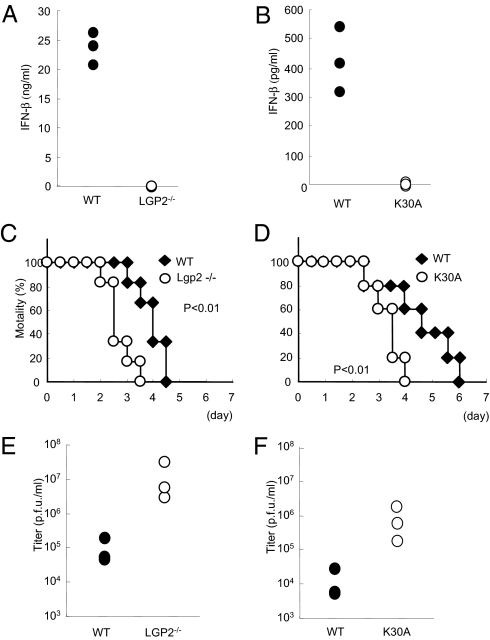
Fig. 6.
Role of LGP2 in host defense against EMCV infection in vivo. (A and B) WT and littermate Lgp2 −/− mice (A) or WT and littermate Lgp2 K30A/K30A (K30A) mice (B) were i.v. inoculated with 1 × 107 pfu EMCV. Serum samples were obtained at 4 h after injection, and the IFN-β concentrations were determined by ELISA. (C and D) Survival rates of WT and Lgp2 −/− mice (C) or WT and littermate Lgp2 K30A/K30A mice (D) intraperitoneally infected with 1 × 102 pfu EMCV were monitored every 12 h for 5 days. (E and F) WT and littermate Lgp2 −/−mice (E) or WT and littermate Lgp2 K30A/K30A mice (F) were infected i.p. with 1 × 102 pfu EMCV. After 48 h, the mice were killed and the virus titers in their hearts were determined by a plaque assay.