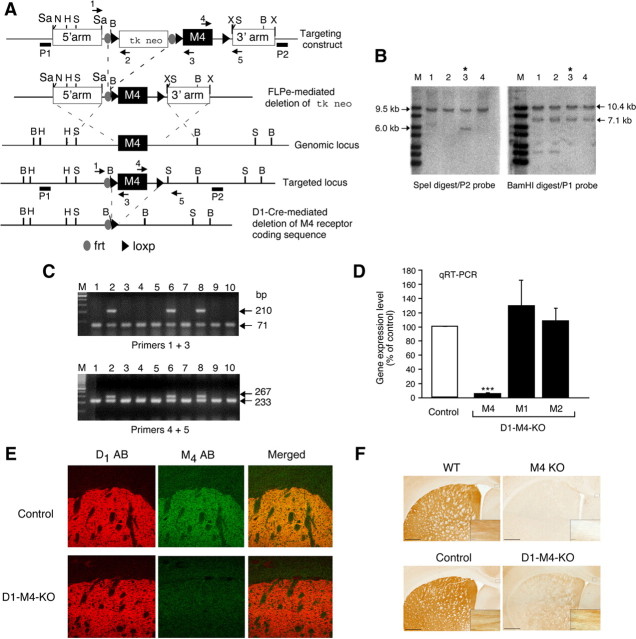
Figure 1.
Strategy used for the conditional deletion of the M4 mAChR gene in D1 dopamine receptor-expressing neurons. A, Partial restriction maps of the wild-type (WT) M4 mAChR genomic locus, targeting construct, recombinant targeted allele, and M4 mAChR-deleted locus. The approximate locations of the frt and loxP sites, the P1 and P2 probes used for Southern analysis (filled bars), and the primers (arrows) used for PCR genotyping studies are indicated. H, HindIII; N, NotI; B, BamHI; X, XhoI; S, SpeI; Sa, SacII. B, Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from representative ES cell clones before FLPe-mediated deletion of the tk/neo cassette. SpeI- or BamHI-digested DNA was analyzed with the P2 and P1 probes, respectively. The 9.5 and 10.4 kb bands indicate the presence of the WT M4 receptor allele, whereas the 6.0 and 7.1 kb bands are diagnostic for the proper integration of the targeting construct. Note that ES cell clone 3 (marked with an asterisk) showed the proper targeting event. C, PCR genotyping analysis of ES cell DNA after FLPe-mediated deletion of the tk/neo cassette. The 71 and 210 kb bands indicate the presence of the WT and the floxed M4 receptor allele, respectively (use of primers 1 and 3, top). Analogously, the 233 and 267 bp bands are diagnostic for the presence of the WT and the floxed M4 receptor allele, respectively (use of primers 4 and 5, bottom). Note that ES cell clones 2, 6, and 8 were heterozygous for the floxed M4 receptor allele. The same strategy was used for the genotyping of mouse tail DNA. D, Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of M1, M2, and M4 mAChR mRNA expression in the striatum of control mice (M4 fl/fl) and D1–M4-KO (M4 fl/fl D1-Cre) mice. Data were normalized by the expression of cyclophilin A, which served as an internal control. Results are shown as relative gene expression levels compared to control mice (100%; means ± SEM; n = 4 per group). ***p ≤ 0.001 versus control. E, Confocal microscopy analysis of M4 mAChR and D1 dopamine receptor expression in the striatum. The three top panels demonstrate that M4 muscarinic and D1 dopamine receptor proteins were colocalized in the striatum of control mice. The three bottom panels indicate that striatal M4 mAChR staining was reduced to background levels in D1–M4-KO mice. F, Immunohistochemical localization of M4 mAChRs in selected brain regions. As expected, M4 mAChR staining was abolished throughout the brain in whole-body M4 receptor KO mice, indicative of the specificity of the M4 mAChR antibody used (top right). The corresponding WT mice gave the expected M4 mAChR staining pattern (top left). In brain sections from WT (control) mice (left), M4 mAChR staining was abundant in the striatum and in presumed axonal processes in the corpus callosum (high-power inset). In the corresponding sections from D1–M4-KO mice (bottom right), M4 mAChR staining was greatly reduced in the striatum, but was retained in other areas of the brain such as the corpus callosum (inset).