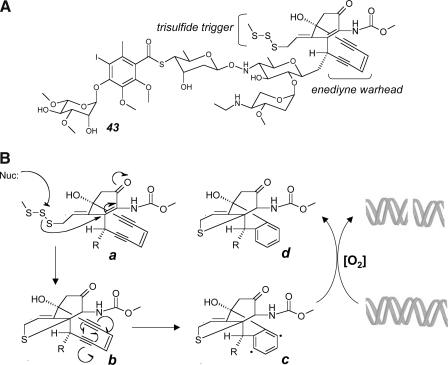
FIG. 7.
Free radical mechanism of DNA cleavage by the polysulfide derivative calicheamicin γ1I. (A) Calicheamicin γ1I (43) with enediyne warhead and trisulfide bioreductive trigger. (B) After intracellular bioreductive activation of the trisulfide trigger by formation of a thiolate intermediate (a), an intramolecular Michael adduction enables subsequent Bergman cycloaromatization of the enediyne warhead (b), leading to the generation of a highly reactive diradical intermediate (c) in close proximity to target DNA. Oxygen-dependent DNA cleavage is initiated by hydrogen abstraction, leading to the formation of an unreactive reaction product (d).