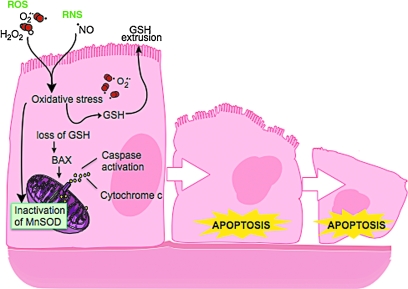
FIG. 14.
Redox abnormalities trigger apoptosis in airway epithelial cells. Exposure to ROS and/or RNS leads to extrusion of intracellular GSH and GSSG, and oxidative modification of MnSOD. Loss of SOD activity and/or extrusion of GSH activates BAX and caspases, and causes cytochrome c release from mitochondria, all of which trigger cell entry into programmed cell death pathways. This mechanism likely contributes to apoptosis and loss of airway epithelial cells, which is a hallmark of the remodeling in the asthmatic airway. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).