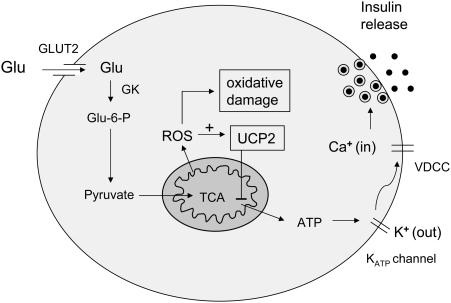
FIG. 8.
Role of mitochondria in regulating insulin secretion. As shown, glucose sensing and glucose-induced insulin release is dependent on mitochondrial ATP generation and affected by both mitochondrial ROS and UCP2. ATP is essential for opening of potassium ATP channels and, therefore, for entry of calcium and insulin release from storage granules. Under conditions of hyperglycemia, it is possible that excess ROS may lead to oxidative damage, gradually impairing insulin secretion over time, with worsening of the diabetic state. +, Positive effect. Dash, Negative effect. VDCC, voltage dependent calcium channel; GK, glucokinase.