Figure 7. Inhibition or silencing of Wee1 sensitizes cells to apoptosis induced by Hsp90 inhibitor.
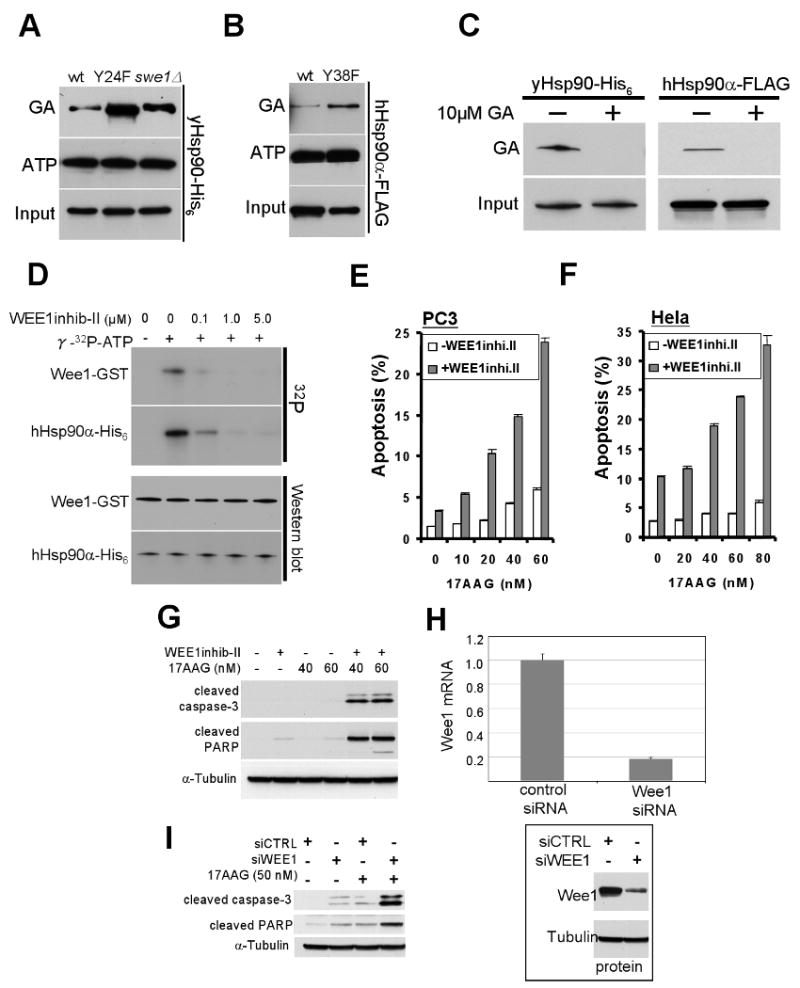
A) GA-bead pulldown of yHsp90 from yeast lysates of wt and swe1Δ cells, or of yHsp90-Y24F mutants; ATP-bead pulldown of yHsp90 from identical lysates is shown for comparison.
B) GA-bead pulldown of hHsp90-Y38F in lysates from mammalian cells. ATP binding is shown for comparison.
C) GA-bead pulldown of yHsp90 from yeast lysate or FLAG-hHsp90α from COS7 cell lysate. Both cell lysates were pre-incubated with 10 μM GA for 15 min prior to GA-bead pulldown to verify GA-bead specificity.
D) Wee1-GST, expressed and purified from insect cells, was used at 0.1 μM in the presence of γ32p-ATP. Wee1 inhibitor concentrations were as shown.
E) PC3 or (F) HeLa cells were treated with 2.5 uM or 5 uM Wee1 inhibitor, respectively, for 24 h. Cells were then treated with indicated concentrations of 17-AAG for an additional 48 h. Apoptosis was detected by FACS analysis as described in Methods.
G) PC3 cells were treated as above, and cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP were detected by immunoblotting.
H) Effectiveness of Wee1 silencing was monitored by mRNA exxpression. Wee1 protein was also visualized by Western blotting with tubulin as loading control.
I) The experiment in (G) was repeated using 50 nM 17-AAG in Wee-1 silenced cells.
