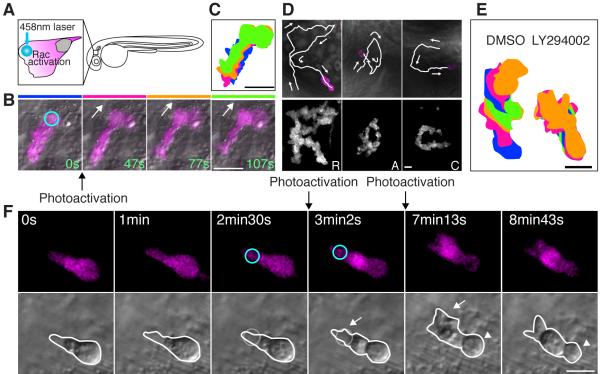
Figure 4.
Photoactivation of Rac at the leading edge can rescue the protrusion defects but not the rounded tail or migration defects induced by PI(3)K inhibition.
(A) A schematic representation of photoactivation of Rac at the neutrophil leading edge in zebrafish. (B) Photoactivation of Rac at the leading edge induces protrusion and migration of a neutrophil in tissues (movie S5). The circle indicates the position of Rac photoactivation. (C) Overlayed images of (B) show directional migration induced by photoactivated Rac. (D) Spelling by neutrophil trajectories guided through repetitive photoactivation of Rac at the leading edge (movie S6). (E) Overlayed images show that PI(3)K inhibition disturbs Rac photoactivation-induced migration (The leading edge was activated for 20 seconds twice during 5 minute imaging). (F) Photoactivation of Rac at the front (circles) can rescue the protrusion defect induced by PI(3)K inhibition (arrows), but not the rounded tail defect (arrowheads) (movie S8). Images are representative of more than 5 time-lapse movies from experiments repeated on at least two separate dates. Scale bars, 20 μm (B, C), 10 μm (D-F).