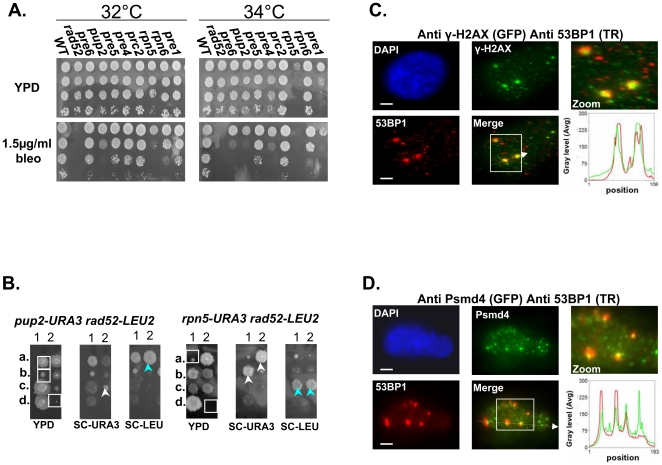
Figure 3. Mutated proteasome subunits affect the repair of DNA DSBs.
(A) Most of proteasomal Ts mutants are sensitive to bleomycin (bleo). Five-fold serial dilutions of the indicated proteasomal subunits mutants were spotted on YPD medium lacking or supplemented with 1.5 µ/ml of bleo. Cells were incubated at 32°C and 34°C to find the semi-permissive temperature of each Ts mutant. (B) rpn5ΔC and pup2 show synthetic growth defect with rad52. To examine whether there could be a link between the proteasome and the repair of DSBs, we created and sporulated heterozygous diploid strains containing Ts alleles of either rpn5ΔC and pup2 combined with rad52. Tetrad dissection showed that Ts alleles of rpn5ΔC and pup2 cause a synthetic growth defect when either one is combined with rad52. The synthetic growth defect of the double mutant spores (encircled by white squares on the YPD plate) is evident when compared to the single haploid mutants (pointed out by white or light blue arrows). (C,D) Protesomal subunits associate with DSB markers in mammalian cells. HeLa cells were treated for 2 hrs with 5 µ/ml of bleo prior to subjection to IIF microscopy. Primary antibodies were recognized with appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated with either Alexa-fluor 488 (GFP filter), or Cy-3 (TR filter). Scale bars, 3 µm. (C) IIF to demonstrate the colocalization pattern of 53BP1 and γ-H2AX in bleo-treated cells. The DSB markers 53BP1 and γ-H2AX show clear co-localization at large foci, likely to represent DSB sites. Red and green curves on the line scan graph represent 53BP1, and γ-H2AX respectively. (D) Representative images demonstrating an association of the RP subunit Psmd4 with DSB sites, represented by the large 53BP1 foci. Red and green curves on the line scan graph represent 53BP1 and Psmd4 respectively.