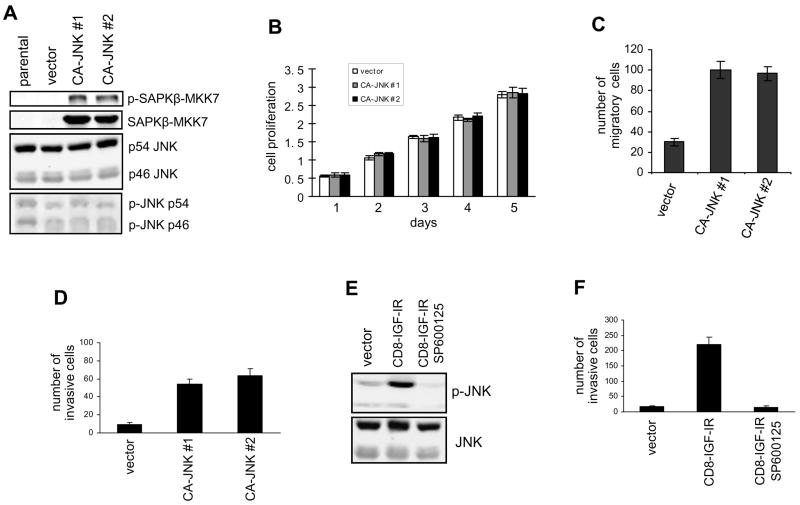
Figure 1.
Hyperactive JNK induces migration and invasion. (A) SAPKβ-MKK7 (CA-JNK, 90 kD) was stably expressed in MDA-MB-468 cells. Its expression was examined by immunoblotting with anti-JNK and anti-p-JNK antibodies. Endogenous JNK (46 and 54 kD) was used as a control. (B) Cell proliferation of MDA-MB-468 cells expressing CA-JNK or the vector was measured using the MTT assay. (C) The Dunn chamber migration assay was conducted with 10% serum medium as a chemoattractant. Migration ability is presented as the increased number of MDA-MB-468 cells detected in the annular bridge region. Each bar represents mean ± SD of samples measured in duplicate. (D) MDA-MB-468 cells expressing CA-JNK or the vector were assayed for their ability to invade a Matrigel matrix coated on the upper-surface of chambers. (E) JNK activation in MCF-10A cells transfected with CD8-IGF-IR or the vector was examined by immunoblotting. The inhibitor SP600125 (5 μM) was used to block JNK activity. (F) The transwell invasion assay was conducted using control and CD8-IGF-IR MCF-10A cells. The effect of SP600125 on invasion was tested.