Fig. 2. Integrated model of influenza A virus host factors.
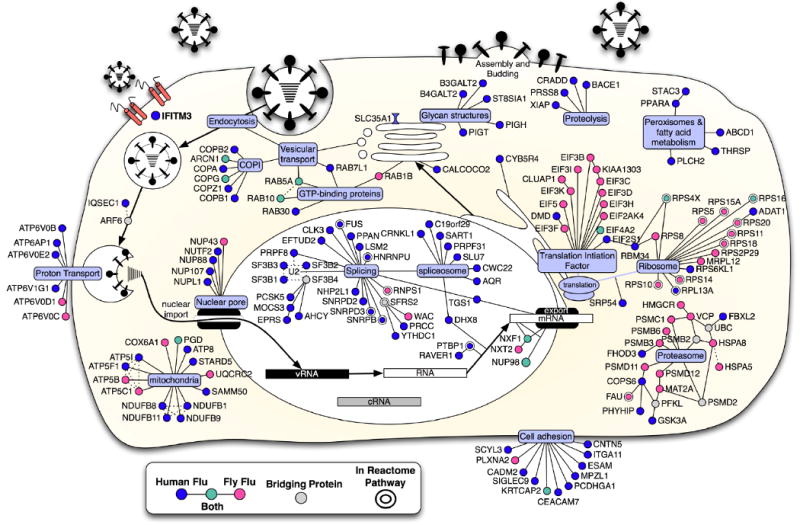
Using the influenza A virus lifecycle as a guide (Lamb and Krug, 2001), the candidate proteins from the human and fly screens were placed at the position most likely to be relevant to the virus using a database of annotations from Gene Ontology, KEGG, Reactome and OMIM (see methods). Computational mapping and supporting evidences were reviewed and refined manually (Dataset S1C-F). The known molecular functions of the host factors were determined with the use of bioinformatics and multiple data sets (gray ovals). Host factors identified in the human siRNA screen (blue); the human orthologues of proteins identified in the fly-based screen (pink), factors which were found in both human and fly screens (green), and bridging proteins that were not detected, but none-the-less generate potentially insightful interactions (gray). Double borders signify the candidate is present in the Reactome influenza A virus infection pathway (Vastrik et al., 2007). Solid lines between genes indicate a protein interaction in human or other speicies. Dotted lines indicate inferred interaction from literature or annotation. Viral RNA (vRNA), viral complementary RNA (cRNA).
