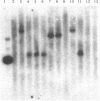
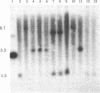
Abstract
The hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (Hprt) gene has been mutated in mouse blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cells by site-directed homologous recombination. Embryonic stem cells were electroporated in the presence of a targeting DNA fragment containing two specific features: (i) The targeting DNA contained a promoterless neomycin phosphotransferase (neo) gene that, when located within the endogenous Hprt locus, could be transcribed from the promoter of the target locus. (ii) The targeting fragment had two short regions of homology with the endogenous Hprt gene: one, 132 base pairs long and the other, 1.2 kilobase pairs long. Targeted cells in which the designed homologous recombination event occurred were isolated either by selection with G418 followed by 6-thioguanine or by selection with 6-thioguanine alone. Even though less than 2 kilobases of homology existed between the exogenous and target DNAs, an average of 2.6 embryonic stem cells were successfully targeted for every 10(5) colonies surviving electroporation. Six of the Hprt- cell lines showed homologous recombination. These six lines were further analyzed by nucleotide sequencing a fragment that spans one crossover point after amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. Four lines had the expected sequence, whereas two lines had small deletions abutting the 132-base-pair region of homology.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Kato S., Camerini-Otero R. D. A pattern of partially homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):206–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayares D., Chekuri L., Song K. Y., Kucherlapati R. Sequence homology requirements for intermolecular recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5199–5203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs S. S., Gregg R. G., Borenstein N., Smithies O. Efficient transformation and frequent single-site, single-copy insertion of DNA can be obtained in mouse erythroleukemia cells transformed by electroporation. Exp Hematol. 1986 Nov;14(10):988–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Modification of DNA ends can decrease end joining relative to homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4959–4963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T., Gregg R. G., Maeda N., Hooper M. L., Melton D. W., Thompson S., Smithies O. Targetted correction of a mutant HPRT gene in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):576–578. doi: 10.1038/330576a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossler A., Doetschman T., Korn R., Serfling E., Kemler R. Transgenesis by means of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9065–9069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Blattner F. R. Lambda Charon vectors (Ch32, 33, 34 and 35) adapted for DNA cloning in recombination-deficient hosts. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Evans M. J. Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Ledbetter D. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T. In vitro translation of hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase mRNA: characterization of a mouse neuroblastoma cell line that has elevated levels of hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6977–6980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molineaux S. M., Engh H., de Ferra F., Hudson L., Lazzarini R. A. Recombination within the myelin basic protein gene created the dysmyelinating shiverer mouse mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E., Bradley A., Kuehn M., Evans M. Germ-line transmission of genes introduced into cultured pluripotential cells by retroviral vector. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):445–448. doi: 10.1038/323445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubnitz J., Subramani S. The minimum amount of homology required for homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2253–2258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Hooper M. L. Buffalo rat liver cells produce a diffusible activity which inhibits the differentiation of murine embryonal carcinoma and embryonic stem cells. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gregg R. G., Boggs S. S., Koralewski M. A., Kucherlapati R. S. Insertion of DNA sequences into the human chromosomal beta-globin locus by homologous recombination. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):230–234. doi: 10.1038/317230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Introduction of homologous DNA sequences into mammalian cells induces mutations in the cognate gene. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):34–38. doi: 10.1038/324034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]