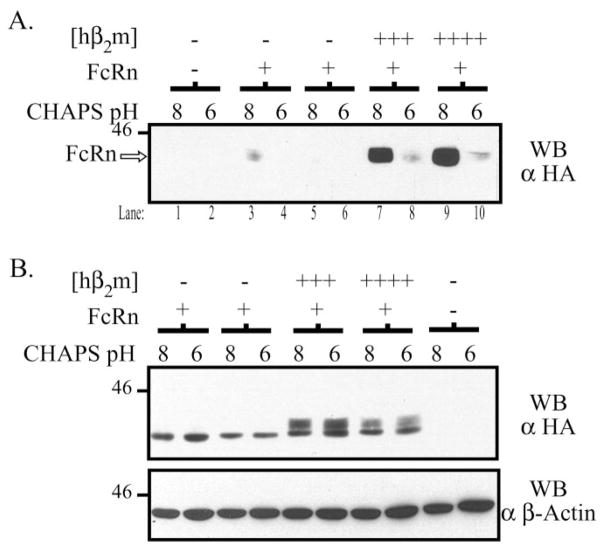
Fig. 8. Surface hFcRn in the presence of co-expressed hβ2m is biochemically functional.
A, subconfluent MDCK clones were biotinylated, lysed in 5 mg/ml CHAPS, pH 6.0 or 8.0, and an IgG binding assay was performed as previously described. The non-binding fraction of each reaction was subsequently precipitated with avidin-agarose at 4 °C overnight. The avidin precipitates were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting for the HA tag as previously described. Samples were as follows: lanes 1–2, both empty vectors; lanes 3–4 and 5–6, FLFcRn#1 and pEF6/V5-HisA, two different clones; lanes 7–8 and 9 –10, FLFcRn#1 and pEF6.hβ2m (hβ2m +++and hβ2m ++++, respectively). B, 20 μg of each lysate was directly analyzed by Western blot for the HA tag to verify that FcRn was equally solubilized at pH 6.0 and 8.0 (top gel). Note the presence of a predominantly fast migrating species of hFcRn in the absence of hβ2m and a fast and slow migrating species of hFcRn in the presence of hβ2m consistent with an immature and mature form of hFcRn, respectively. This blot was then stripped and reprobed for β-actin. The images are the results of one representative experiment (n = 4). The molecular mass in kilodaltons is indicated on the left of each gel.