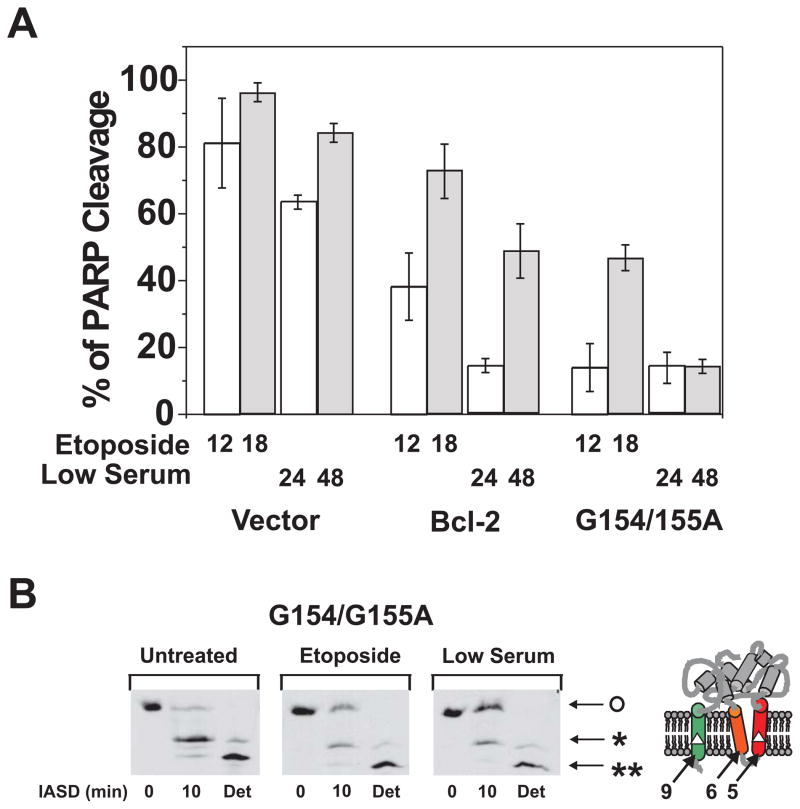
Fig. 5. Effect of mutations in helix 5 on the anti-apoptosis activity and conformational alteration for Bcl-2.
A. The anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-2 or the G154/155A mutant was assayed after addition of etoposide for 12 (open bar) or 18 hr (shaded bar) or growth in low serum for 24 (open bar) or 48 hr (shaded bar) by measuring PARP cleavage. Rat-1MycERTAM cells were infected with packaged retroviral vector, or vector that expresses wild-type human Bcl-2 or Bcl-2-G154/155A, as indicated. Clones were selected that stably expressed equivalent amounts of the two proteins and then assayed for resistance to etoposide or serum starvation as indicated below the bars. Data shown are averages of three independent experiments with S.D. (error bars). B. The conformational alteration of Bcl-2 or the G154/155A mutant induced by the etoposide treatment or serum starvation was monitored by protection from IASD labeling assayed by isoelectric focusing followed by immunoblotting for human Bcl-2. Modification with IASD adds two negative charges at each cysteine modified and results in a discrete shift in mobility during isoelectric focusing. The cysteines available for modification in helix 5 and 9 are indicated as white triangles on diagram to the right of the panels. The migration position before IASD labeling (IASD, 0 min) indicates the migration position of the unlabeled protein (O). The migration position after labeling with detergent added to solubilize the membrane (Det) indicates the migration position of the protein labeled at both cysteines (**). Labeling of a single cysteine (Cys158 in helix 5) results in a band with intermediate migration (*; IASD, 10 min). In untreated cells Bcl-2 has not changed conformation and the major band (*) after IASD labeling represents protein in which Cys158 is labeled but Cys229 in helix 9 is protected unless detergent is added (Det). After treatment with etoposide or low serum the relative intensity of the unlabeled band (O) increases indicating protection of both cysteines from IASD. Addition of detergent renders both cysteines accessible to the reagent confirming that protection from IASD was due to insertion of the cysteines into the bilayer. The predicted topology of Bcl-2 with both cysteines protected from IASD is shown to the left of the panel with helices 9, 6 and 5 indicated.