Figure 8.
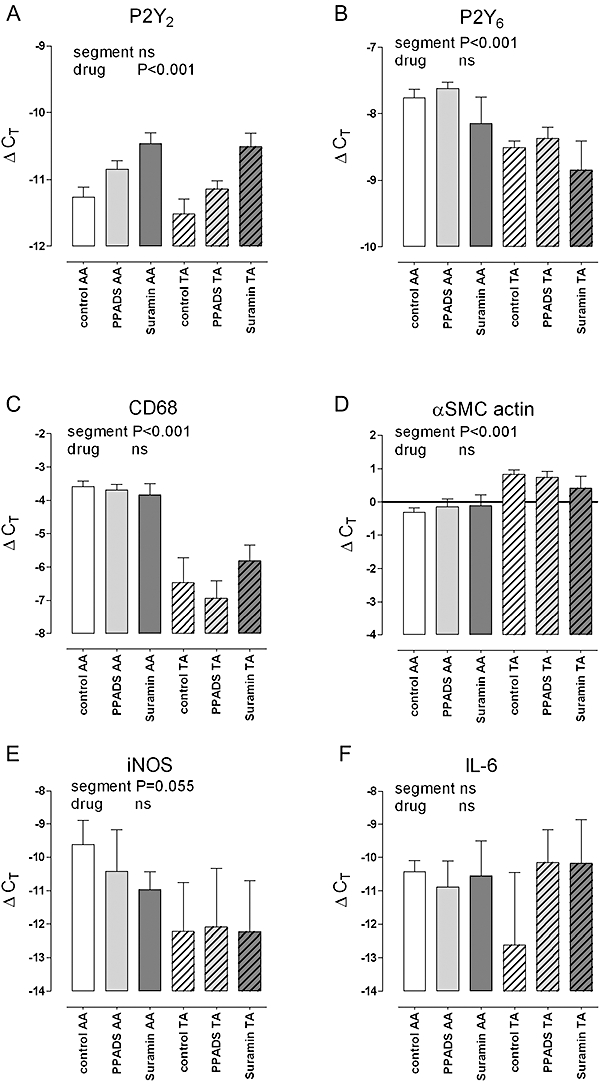
mRNA expression of P2Y2 receptors (A), P2Y6 receptors (B), the macrophage marker CD68 (C), α-SMC actin (D), iNOS (E) and IL-6 (F) in the atherosclerotic aortic arch (AA) and in virtually plaque-free thoracic aorta (TA) segments of control mice and apoE–/– mice (4 months), on a Western-type diet, treated with suramin or PPADS. Atherosclerotic AA segments showed increased mRNA expression of P2Y6 receptors, CD68 and iNOS (tendency), unaltered expression of P2Y2 receptors and IL-6, and slightly decreased α-SMC actin mRNA. Treatment with suramin or PPADS increased mRNA of P2Y2 receptors and showed a tendency to decrease iNOS activation, whereas the expression of P2Y6 receptors, CD68, α-SMC actin and IL-6 were not influenced by the purinoceptor antagonists. Results show mean and SEM, n= 6. Significances of a factorial anova with segment (AA or TA) and drug treatment as factors are shown; the interaction term was never significant. IL-6, interleukin 6; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; PPADS, pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2′-4′-disulphonic acid; SMC, smooth muscle cell.
