Figure 4.
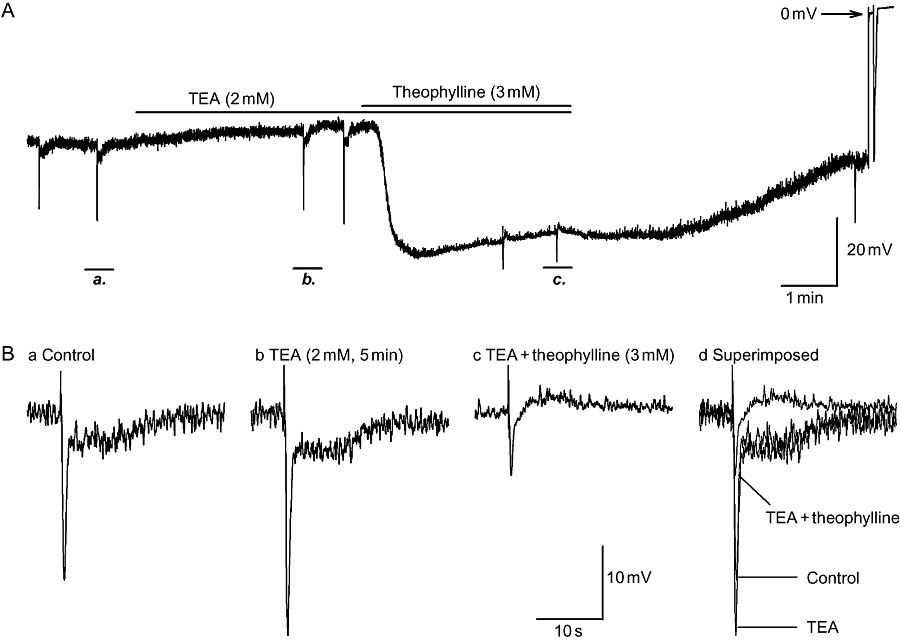
Failure of tetraethylammonium (TEA), a Ca2+-activated large-conductance K+ channels (BK) channel blocker, to prevent the inhibitory effects of theophylline on electrical properties. (A) Continuous recording of the effects of pre-application of TEA (2 mM, 5 min) on the inhibition induced by theophylline (3 mM, 5 min). (B, panels a–c) Inhibitory junction potentials (IJPs) from panel A at an expanded time scale in control, TEA and TEA plus theophylline. TEA failed to prevent the hyperpolarization and abolition of nitrergic IJPs, suggesting that the inhibitory effects of theophylline were not due to the opening of BK channels.
