Figure 7.
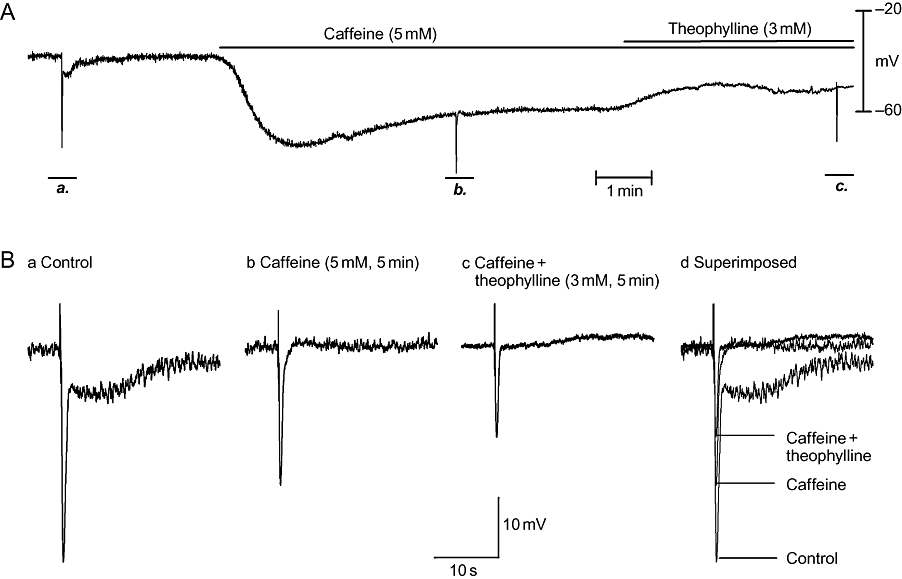
Pre-application of caffeine prevented the resting membrane potential (RMP) hyperpolarization induced by theophylline. In panel A, an experimental recording is shown of the effects of theophylline (3 mM, 5 min) in the presence of caffeine (5 mM, 5 min). Caffeine hyperpolarized the RMP and abolished nitrergic inhibitory junction potentials (IJPs). Further application of theophylline produced RMP depolarization rather than hyperpolarization. (B, panels a–c) IJPs (on an expanded time scale) before and after administration of caffeine and theophylline. (B, panel d) Overlapped IJPs in comparison.
