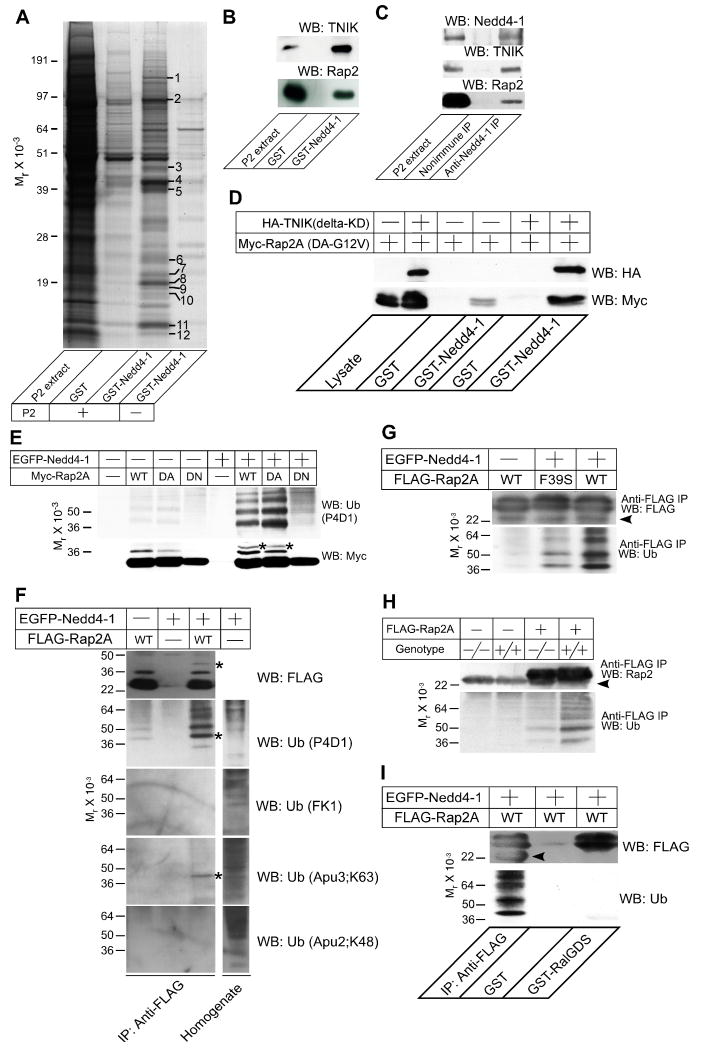
Figure 5. Rap2 is a Target of Nedd4-1.
(A) Affinity purification of TNIK as a binding partner of Nedd4-1. 40 μg of GST or GST Nedd4-1 (residues 217-549) were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose beads and a Triton X-100 extract of rat brain synaptosomes (P2 extract, +) or buffer (-) were applied. After washing the beads, bound proteins were eluted with 1 M NaCl. Protein bands that appeared to be enriched in the eluate from the GST Nedd4-1 column were analyzed by mass spectrometry. Protein identification was successful for the twelve marked bands. The results of the mass spectrometric analysis are given in Table S4.
(B) Complex formation of Rap2 with TNIK and GST-Nedd4-1. Samples eluted from the Nedd4-1 beads (see A) were blotted for TNIK (top) and Rap2 (bottom). Neither antibody cross-reacted with samples purified on GST beads that were used as a negative control.
(C) Complex formation of endogenous Rap2, TNIK, and Nedd4-1. Nedd4-1 was immunoprecipitated using a rabbit polyclonal anti-Nedd4-1 antibody from mouse brain membranes after treatment with a thiol-cleavable chemical crosslinker. Precipitates were boiled in Laemmli buffer with 50 mM DTT, loaded to SDS-PAGE gels, and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Nedd4-1, anti-TNIK, or anti-Rap2 antibodies. Note that TNIK and Rap2 were coimmunoprecipitated with Nedd4-1 but not with the negative control IgG.
(D) TNIK dependent interaction of Rap2A with Nedd4-1. GST or GST-Nedd4-1 (residues 217-549) were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose beads and recombinant Myc-Rap2A(DA-G12V) was loaded in the presence (+) or absence (-) of HA-TNIK (delta-KD). Interaction was detected by Western blotting using anti-HA or anti-Myc antibodies.
(E) Ubiquitination of Rap2A by Nedd4-1. EGFP-Nedd4-1 (+) or EGFP alone (-) were coexpressed with WT, dominant active (DA), or dominant negative (DN) mutants of Myc-tagged Rap2A. Myc-Rap2A was immunoprecipitated using an anti-Myc antibody. Immunoprecipitates were blotted for Myc (lower panel) and ubiquitin (upper panel).
(F) Mono- and di-ubiquitination of Rap2A by Nedd4-1. FLAG-Rap2A was immunoprecipitated from HEK cells expressing FLAG-Rap2A with or without EGFP-Nedd4-1. FLAG-Rap2A was eluted from anti-FLAG antibody coupled beads with 3×FLAG peptides and immunoblotted using four different monoclonal mouse or rabbit anti-ubiquitin antibodies, P4D1, FK1, Apu3, and Apu2. P4D1 recognizes both poly- and monoubiquitin conjugated proteins while FK1 recognizes only polyubiquitin conjugated ones. Apu3 and Apu2 recognize K63-linked and K48-linked polyubiquitin chains, respectively. The lysate of HEK cells overexpressing EGFP-Nedd4-1 was also blotted using the four anti-ubiquitin antibodies in order to show that the antibody titers are comparable.
(G) Loss of TNIK interaction in the F39S point mutant of Rap2 reduces the ubiqutination of Rap2 by Nedd4-1. WT or F39S point mutant FLAG-Rap2A were overexpressed in HEK cells together with EGFP (-) or EGFP-Nedd4-1 (+). Efficiencies of immunoprecipitation of FLAG-Rap2A were comparable as seen in the Western blot using the anti-FLAG antibody (upper panel). FLAG-Rap2A(F39S) showed clearly weaker intensities of ladder patterns than FLAG-Rap2A(WT) in the blot using the anti-ubiquitin antibody (lower panel).
(H) Ubiquitination of Rap2A by endogenous Nedd4-1 and ubiquitin. WT (+/+) and Nedd4-1-KO (-/-) MEFs were transfected with a mammalian expression vector encoding FLAG-Rap2A. Proteins from lysed cells were immunoprecipiated with an anti-FLAG antibody and blotted for Rap2A with an anti-Rap2 antibody (upper panel) and an anti-ubiquitin antibody (lower panel).
(I) Ubiquitination of Rap2A blocks the Rap2A function. FLAG-Rap2A(WT) expressed in HEK cells together with EGFP-Nedd4-1 was precipitated using anti-FLAG antibodies (first lane) or GST-RalGDS-coupled beads (third lane), and blotted for FLAG (upper panel) or ubiquitin (lower panel). Note that ubiquitinated FLAG-Rap2A was efficiently precipitated only with the anti-FLAG antibody while total amounts of precipitated FLAG-Rap2A were comparable between lanes 1 and 3.
Arrowheads in (G-I) indicate the light chain of the anti-FLAG IgG used for immunoprecipitation. All results shown are representative of two to three independent experiments. Asterisks in (E) and (F) indicate bands with a molecular weight corresponding to Myc-Rap2A or FLAG-Rap2A conjugated with two ubiquitin moieties.
See also Figures S1, S5, and S6, and Table S4.