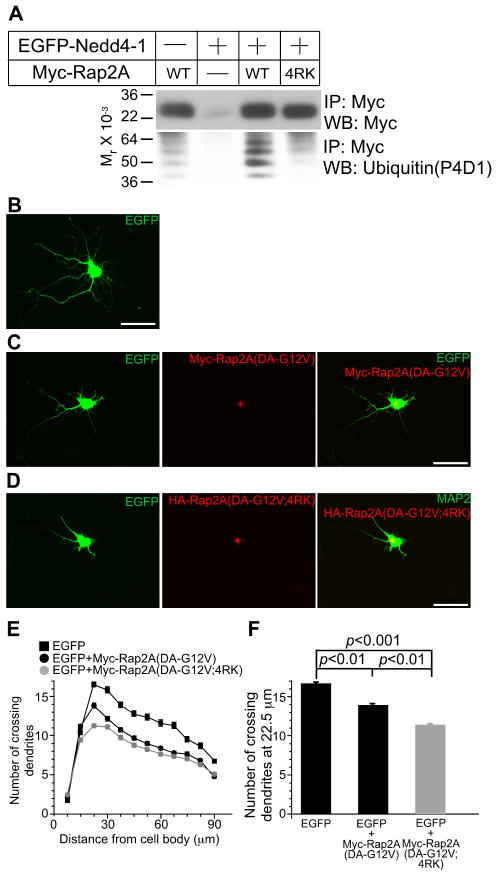
Figure 7. Perturbation of Ubiquitination of Rap2A Enhances Rap2A Function in Cultured Neurons.
(A) HEK cells were transfected with Myc-tagged WT or 4RK mutant variants of Rap2A, with or without EGFP-Nedd4-1. Myc-Rap2A was immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibodies, and ubiquitination was detected with the anti-ubiquitin P4D1 monoclonal antibody (Jura et al., 2006).
(B-D) Overexpression of Myc-Rap2A(DA-G12V;4RK) reveals a gain-of-function phenotype. Myc-Rap2A (DA-G12V) and EGFP coexpressing neurons shows impaired development of neurites as compared to EGFP expressing neurons (B, C). This effect of Rap2A was more pronounced when Myc-Rap2A(DA-G12V;4RK) was coexpressed with EGFP (D). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(E) Sholl analysis of Rap2A overexpressing neurons. Black rectangles, EGFP- expressing neurons (n=80); black circles, EGFP- and Myc-Rap2A(DA-G12V) coexpressing neurons (n=109); gray circles, EGFP- and Myc-Rap2A(DA-G12V;4RK) coexpressing neurons (n=109).
(F) Numbers of crossing dendrites at 22.5 μm from the cell body in EGFP-, EGFP- and Myc-Rap2A(G12V)-, or EGFP- and Myc-Rap2A(DA-G12V;4RK)-over expressing neurons. Nonparametric ANOVA test revealed a significant effect of expression of Myc-Rap2 mutants (p<0.0001). Dunn's multiple comparisons test revealed significant differences between groups linked with black lines.
See also Figures S6-S8 and Table S2.