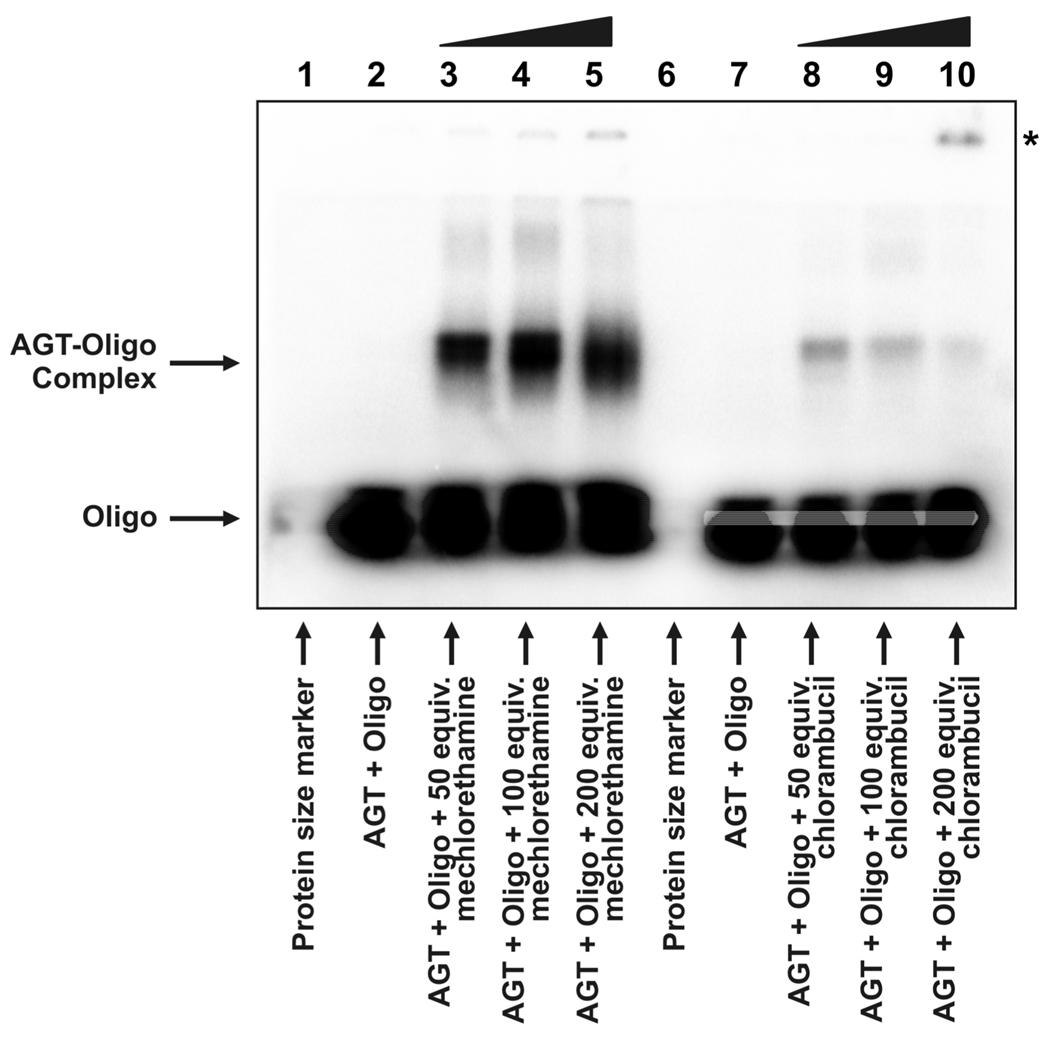
Figure 1.
Detection of drug-induced AGT-DNA cross-links. Recombinant human AGT protein and radioactive duplex oligodeoxynucleotide (see Materials and Methods) were incubated in the presence of 50 (lanes 3 and 8), 100 (lanes 4 and 9) or 200 (lanes 5 and 10) equivalents of mechlorethamine (lanes 3–5) or chlorambucil (lanes 8–10) and subsequently resolved by 12% SDS-PAGE. Free duplex DNA (labeled 'Oligo') migrated to the bottom of the gel, whereas DNA cross-linked to AGT (labeled 'AGT-Oligo complex') displayed a substantially reduced mobility. The mobility of the higher-order complex of drug and AGT is indicated by an asterisk (see text).