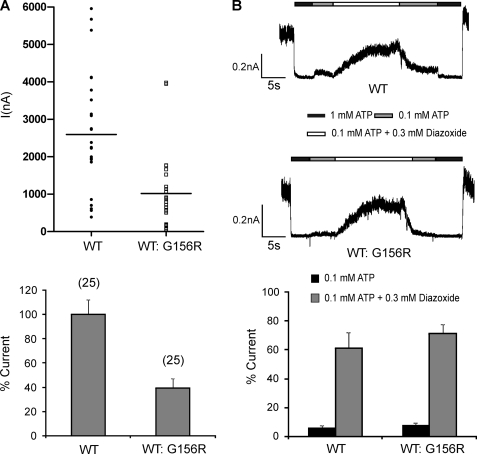
FIGURE 2.
Simulated heterozygous expression of G156R. COSm6 cells were transfected with G156R and WT Kir6.2 cDNA at a 1:1 cDNA ratio (denoted as WT:G156R) together with SUR1 cDNA to simulate heterozygous expression of the mutant Kir6.2 in patients. A, current density was estimated from isolated membrane patches using patch pipettes with closely matched sizes. Twenty-five patches each of WT- or WT:G156R-expressing cells from three-independent experiments were recorded. Top, shown are amplitude distributions of ATP-sensitive potassium currents (I). Bottom, shown is the averaged current amplitude normalized to that of WT-expressing cells. B, shown is a comparison of diazoxide response in channels recorded from WT- and WT:G156R-expressing cells. Top, representative current traces show the stimulatory effect of diazoxide. Patches were exposed to K-INT solutions containing differing concentrations of ATP or diazoxide, as indicated by the bars above the current traces. Free Mg2+ concentration in all solutions was ∼1 mm. Bottom, shown is quantification of averaged diazoxide response. Channel activities observed in 0.1 mm ATP or 0.1 mm ATP + 0.3 mm diazoxide were expressed as the percent current of channel activity observed in K-INT solution (currents in 1 mm ATP were subtracted as background).