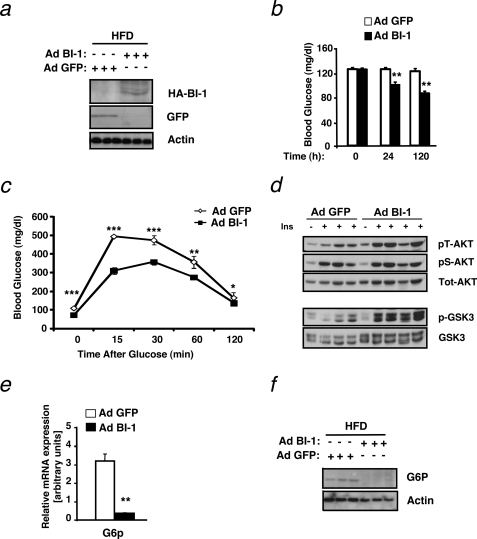
FIGURE 2.
Hepatic BI-1 overexpression ameliorates HFD-induced insulin resistance and glucose metabolism. a, immunoblot analysis was performed for BI-1 or GFP and actin in liver lysates from mice provided HFD and infected with Ad BI-1 or Ad GFP. Livers were collected from mice after an overnight fast, and proteins were extracted and processed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each lane represents liver lysates from a different mouse. b, shown are blood glucose concentrations (mg/dl) in HFD-fed mice immediately before and 24 and 120 h after adenovirus treatment. The results are the mean ± S.E. of n = 9 mice per group (**, p ≤ 0.01). c, glucose tolerance tests (0.5 g/kg, intraperitoneal) were performed on HFD-fed mice 60 h after adenovirus injection. Results are given as the mean ± S.E., n = 9 per group (*, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001). d, shown is insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of AKT (Ser-473 and Thr-308) and GSK3 was measured in liver tissues of Ad BI-1- and Ad GFP-treated HFD-fed mice upon intravenous insulin (Ins, 13 milliunits) injection. e, shown is relative expression of G6p mRNA in the liver of Ad BI-1- or Ad GFP-infected HFD-fed mice (n = 5 per group; **, p ≤ 0.01). f, G6P and actin protein levels in the liver of Ad BI-1- or Ad GFP-infected HFD-fed mice are assessed by immunoblotting (n = 3 of each group).