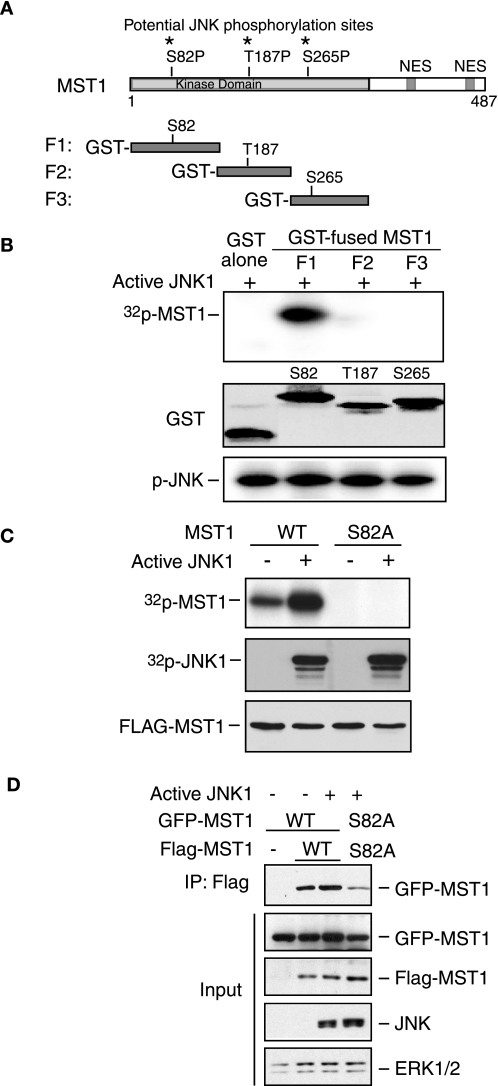
FIGURE 3.
JNK phosphorylates MST1 at serine 82. A, three potential JNK phosphorylation sites in the N terminus of MST1 are indicated. NES, nuclear- exporting sequence. B, in vitro JNK kinase assay was performed by incubating the recombinant active JNK with different GST-fused MST1 fragments (P1, P2, and P3) or GST only as substrate in the presence of [32P]ATP. The reaction was analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. GST protein expression of MST1 and autophosphorylation of JNK are shown in the middle panel and lower panel, respectively. The phosphorylation site of MST1 by JNK kinase is in the P1 fragment. C, in vivo labeling was performed according to the “Experimental Procedures” after co-transfection with active JNK and MST1 in COS7 cells. The membrane was exposed to X-films after electrophoresis (upper panel). The expression of JNK or MST1 is shown in the lower panels. D, lysates of 293T cells transfected with GFP-MST1 (WT or S82A) and FLAG-MST1 (WT or S82A) together with an expression vector encoding active JNK1 or the control vector were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and blotted with GFP antibody. The input was blotted with GFP, FLAG, JNK, or Erk1/2 antibody. MST-S82A mutants confer a lower capability of dimerization.