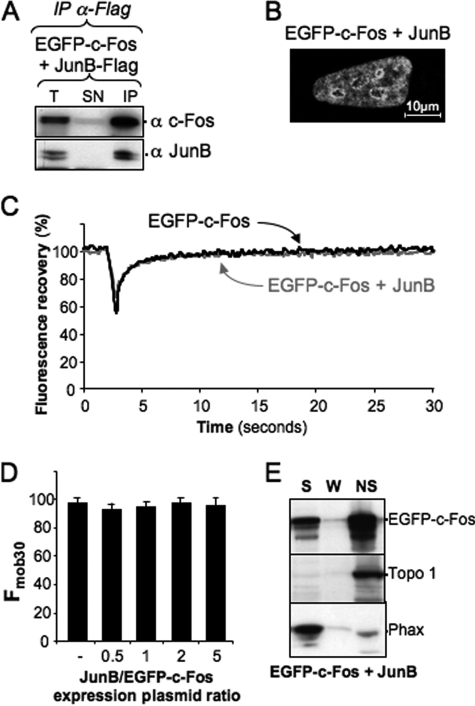
FIGURE 4.
Effect of JunB on c-Fos intranuclear distribution and mobility. A, heterodimerization of JunB-FLAG with EGFP-c-Fos. The expression plasmid for EGFP-c-Fos was transfected in HeLa cells in the presence of a 2-fold excess of JunB-FLAG construct. Co-immunoprecipitations were conducted with the anti-FLAG antibody as in Fig. 3D. The antibodies used in immunoblotting analyses are indicated. B, intranuclear distribution of EGFP-c-Fos in the presence of JunB. EGFP-c-Fos localization in the presence of JunB-FLAG was assessed by confocal microscopy on living cells. The JunB versus EGFP-c-Fos expression plasmid ratio was of 2. C, FRAP experiments. FRAP experiments were conducted in HeLa cells transfected with expression plasmids for either EGFP-c-Fos or EGFP-c-Fos + JunB. In the latter case, the plasmid ratio was 2. The curves correspond to the averages of 20 FRAP experiments in each case. D, mobility of EGFP-c-Fos in the presence of different amounts of JunB. HeLa cells were transfected in the presence of different ratios of JunB versus EGFP-c-Fos plasmids as indicated. Fmob30 were calculated from 15–20 FRAP experiments in each case. E, cell fractionation experiments. Cell fractionation experiments of cells transfected with plasmids encoding JunB and EGFP-c-Fos in a ratio of 2 were conducted and analyzed as in Fig. 1D. T, total cell extract; SN, supernatant; IP, immunoprecipitation; S, soluble; W, wash; NS, nonsoluble.