FIGURE 9.
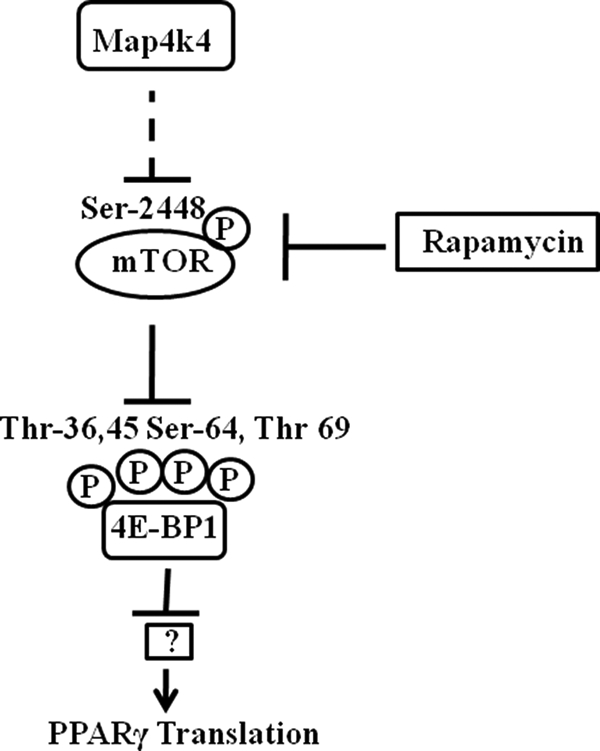
Model for Map4k4-mediated PPARγ protein regulation. Our data support the following hypothesis. Silencing Map4k4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes using siRNA enhances mTOR activity, as indicated by an increase in phosphorylation at Ser-2448. This in turn inhibits 4E-BP1 activity by enhancing phosphorylation at Thr-36, Thr-45, Ser-64, and Thr-69. Phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 renders it inactive leading to its dissociation from the translational initiation factor eIF4E. Thus eIF4E is activated, and cap-dependent translational initiation, responsible for the increase in PPARγ protein levels, is enhanced. However, 4E-BP1 silencing alone does not mimic Map4k4 depletion but blocks the Map4k4 effect, indicating it plays an additional role in regulation of PPARγ protein expression.
