FIGURE 10.
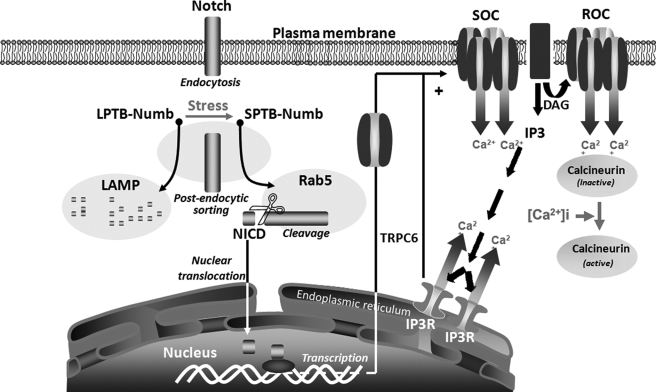
A schematic diagram summarizing the isoform-specific effects of the Numb proteins on the activation of the Notch pathway and the regulation of cellular Ca2+-regulating systems in PC12 cells under stress conditions. In addition to activation of the Notch pathway, trophic factor withdrawal-induced stress promotes an early switch in the expression of the alternatively spliced Numb isoforms that differentially modulate Notch signaling strength. Whereas the LPTB-Numb isoforms reduce the dwelling time of the internalized Notch in Rab5-labeled early endosomes, the SPTB-Numb proteins increase the retention of Notch and its processing to NICD in these endocytic compartments. Consequently, the stress-induced accumulation of Numb-SPTB promotes NICD-dependent transcription of TRPC6, which assembles into native ROCs and SOCs on the plasma membrane. Increased Ca2+ entry through these channels leads to the subsequent activation of calcineurin in cells expressing the SPTB-Numb isoforms.