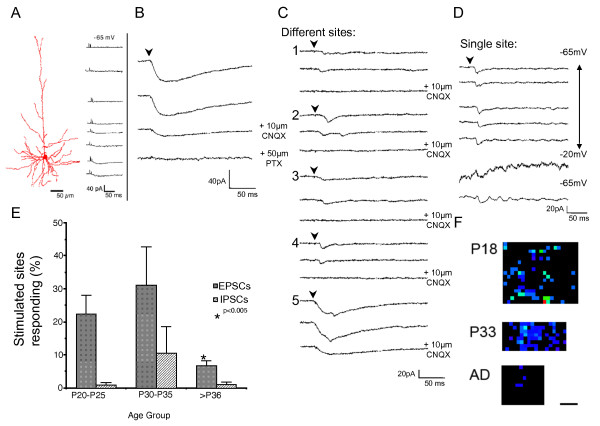
Figure 6.
Uncaging GABA generates excitatory inputs in brain slices from immature animals. (A) Left: camera lucida reconstruction of a biocytin filled neuron in a coronal brain slice. Right: responses of neuron shown in A to uncaging of GABA at locations along its apical and basal dendrites. (B) Effects of picrotoxin (50 mM) and CNQX (10 mM) treatment on the response of a cell to uncaging of GABA close to the cell soma. (C) Effects of CNQX blockade on photostimulation-evoked responses from distant uncaging of GABA. Locations 1 to 4 are >200 μm from the location of the cell body of the recorded neuron. Location 5 is near to the neuron. CNQX blocks the synaptic response, but not the photostimulation-evoked GABA-mediated current. (D) The same locations stimulated a number of times at different holding potentials with uncaging of GABA in a neuron. (E) Graph of the percent of sites stimulated with uncaged GABA in tangential brain slices that generate a synaptic response at different ages. (P20 to P25, n = 11 cells, 348.5 ± 52.8 stimulated sites; P30 to 35, n = 12 cells, 316.6 ± 44.2; <P36, n = 15 cells, 280.5 ± 57.4). Error bars = standard error of the mean. (F) Examples of PSC maps evoked with uncaging of GABA. P20 map consists of 482 stimulated sites covering an area of 0.82 mm2. P34 map consists of 428 stimulated sites covering an area of 0.34 mm2. Mature map consists of 239 stimulated sites covering an area of 0.30 mm2. Scale bar = 250 μm.