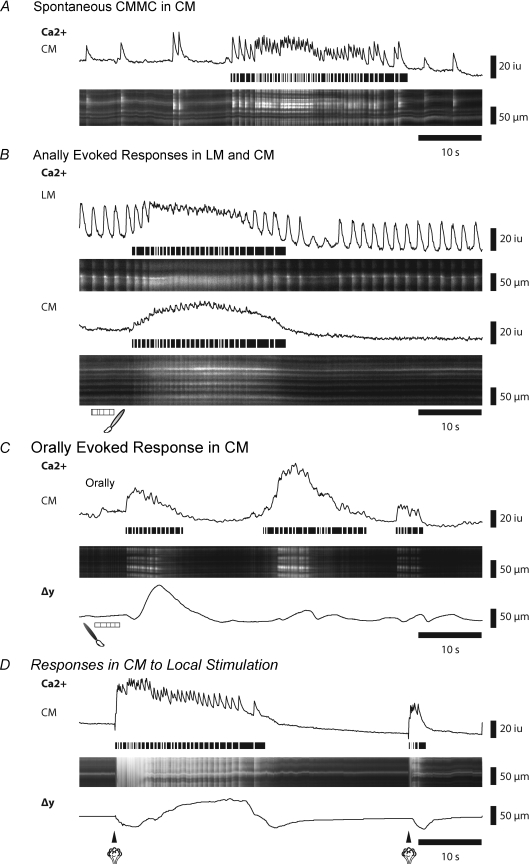
Figure 2. Spontaneous and evoked muscle responses during CMMCs.
A, Ca2+ activity in the circular muscle (CM) during a spontaneous CMMC. The line trace corresponds to activity in ST map. Horizontal lines below transients trace the occurrence of fast Ca2+ transients in the muscle during the CMMC. B, Ca2+ activity in both the longitudinal muscle (LM) and the CM following an evoked CMMC initiated by stimulating the mucosa at the anal end of the preparation. C, Ca2+ activity in the CM following an evoked CMMC initiated by stimulating the mucosa at the oral end of the preparation. Δy shows the displacement (contraction) of the tissue. D, Ca2+ activity in the CM after stimulating the mucosa with a puff of nitrogen directly under the recording site. Note that a second stimulus generates an aborted response.