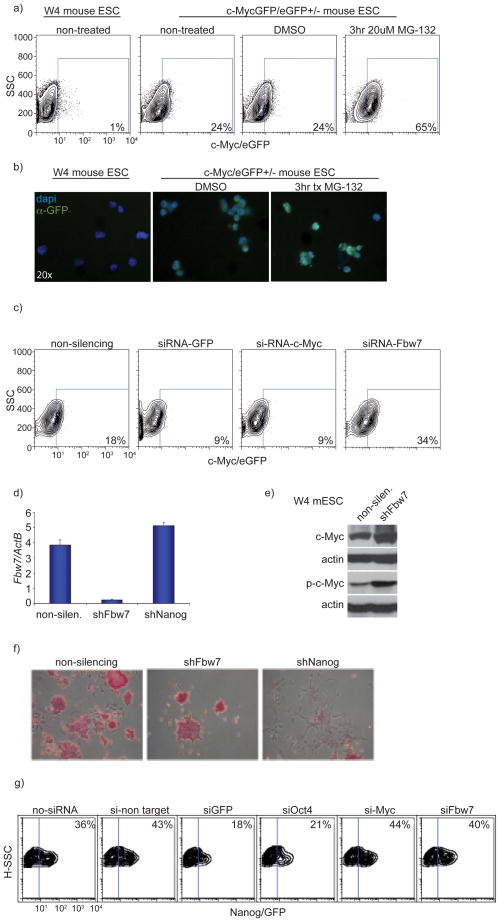
Figure 8. Fbw7 is dispensable for the self-renewal of Murine ESCs.
a) Inhibition of proteasomal degradation via MG-132 treatment resulted in accumulation of c-Myc protein in MyceGFP/− Murine ESCs. b) Visualization of c-Myc-eGFP in W4 and MyceGFP/− Murine ESCs with and without treatment with MG-132. GFP (green), nuclear staining (DAPI) c) Knock-down of Fbw7 using siRNA in c-MyceGFP/− ESCs resulted in accumulation of c-Myc protein (increase in eGFP levels) while siRNA targeting both Myc and GFP showed a reduction in c-Myc-eGFP levels as assessed by FACs analysis. d) qRT-PCR of Fbw7 mRNA expression in ESCs expressing shRNAs against Fbw7 and Nanog. A non silencing shRNA is used as a control. e) Western blot depicting accumulation of both phospho (T58)-and total-c-Myc protein upon shRNA mediated knock down of Fbw7 when compared to a non-silencing shRNA control. f) Alkaline phosphatase staining in Murine ESCs showed no difference in differentiation capacity upon shRNA mediated knock-down of Fbw7 when compared to non-silencing control while silencing of Nanog resulted in complete differentiation. g) siRNA knock-down of Fbw7 in a Nanog-eGFP reporter ESC line resulted in no difference in Nanog-eGFP expression levels when compared to non-silencing control. Knock-down of Oct4 resulted in a reduction of Nanog-eGFP expression levels (marking differentiation). Plots are a representation of at least 3 independent experiments