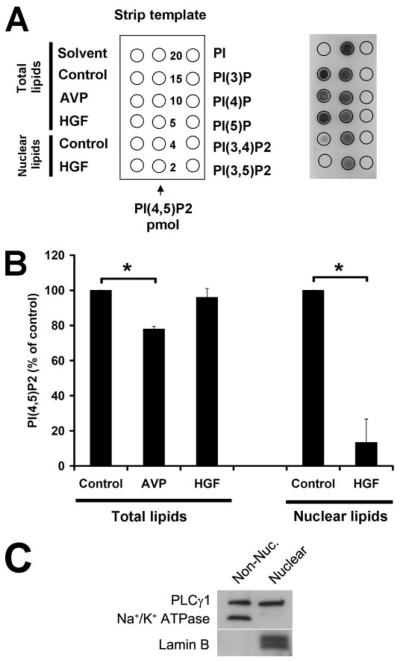
FIGURE 6. HGF hydrolyzes nuclear PIP2.
A, lipid samples were spotted onto nitrocellulose membranes (right), as illustrated by the strip template (left), and the PIP2 levels were detected using an anti-PIP2 monoclonal antibody that reacts with PIP2 with a high degree of specificity. Left column, experimental samples; middle column, PIP2 standards; right column, PIP controls (20 pmol each). PI(3)P, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate; PI(4)P, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate; PI(5)P, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate; PI(3,4)P2, phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate; PI(3,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate; and PI(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. B, densitometric measurement shows that AVP hydrolyzes 22 ± 2% of PIP2 in whole cell preparations (n = 3, *, p < 0.05), whereas HGF stimulation does not hydrolyze significant amounts of PIP2 in such preparations. However, upon HGF stimulation, PIP2 levels in the nucleus are decreased by 87 ± 13% (n = 3, *, p < 0.05). Total lipids and nuclear lipids were isolated 4 min after stimulation with HGF (100 ng/ml) or 30 s after stimulation with AVP (100 nm). Values mean ± S.E. C, phospholipase C-γ1 is found in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus of SkHep1 cells. Non-Nuc., non-nuclear.