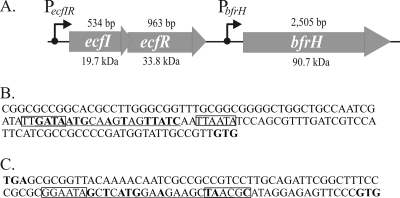
FIG. 1.
Genetic organization of the ecfIR-bfrH locus. (A) Schematic arrangement of the ecfIR-bfrH locus in B. bronchiseptica. ecfI and ecfR encode a putative ECF sigma factor and a putative sigma factor regulator, respectively. bfrH exhibits homology to genes for OM proteins involved in siderophore uptake. The length of each ORF is denoted above the gene; the molecular mass of each of the predicted polypeptides is denoted below the gene. Positions of the two putative promoters, PecfIR and PbfrH, and the direction of transcription are denoted by arrows. (B) Sequences at PecfIR. This promoter contains regions homologous to σ70-type promoters. Putative −10 and −35 regions of PecfIR are boxed. Sequences homologous to the consensus Fur box of E. coli are underlined; nucleotides in bold are perfectly conserved in RB50 and in the consensus Fur box of E. coli. The translational GTG start codon of ecfI is denoted in bold. (C) Sequences at PbfrH. This region contains homology to other ECF sigma factor-regulated promoters. Putative −10 and −35 regions of PbfrH are boxed. Sequences homologous to the consensus Fur box of E. coli are underlined; nucleotides in bold are perfectly conserved in RB50 and in the consensus Fur box of E. coli. The translational stop codon of ecfR and the translational start codon of bfrH are denoted in bold.